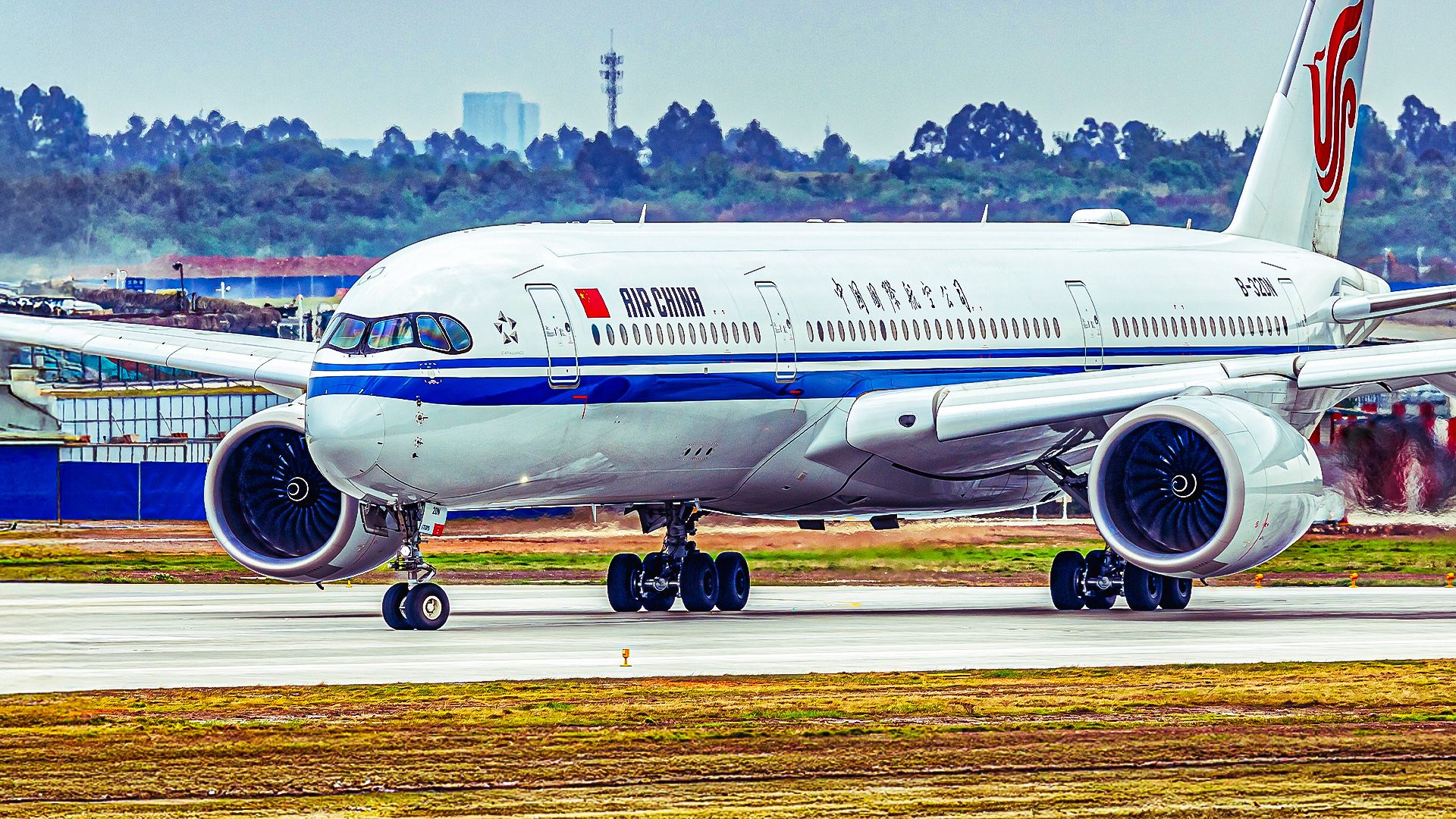
The United States is considering a proposal that could significantly alter the operations of Chinese airlines by restricting their ability to fly over Russian airspace. This initiative, backed by the Department of Transportation, aims to address the competitive imbalance that has arisen since Russia closed its airspace to airlines from Western-friendly nations in response to the ongoing conflict in Ukraine.
As a result of Russia’s decision, US and European carriers have been forced to reroute flights to Asia, leading to longer and more expensive journeys. These detours increase fuel consumption and operational costs, making it more challenging for airlines like United Airlines, Delta Air Lines, and American Airlines to compete effectively. Meanwhile, Chinese carriers, including China Eastern Airlines, China Southern Airlines, and Air China, have continued to benefit from the ability to overfly Russia, allowing them to offer shorter and cheaper flights between East Asia and the United States.
Proposal Details and Industry Reactions
The proposed rule, reported by Reuters, has drawn criticism from several major Chinese airlines, which argue that such a ban would lead to increased flight times of two to three hours on key routes. China Eastern highlighted that extended travel times would raise operational costs and fuel consumption, jeopardizing the convenience of air travel for many passengers. The airline also projected that the new regulations could necessitate rebooking for approximately 2,800 travelers during the holiday season between November 1 and December 31.
Additionally, United Airlines has urged the administration to extend similar restrictions to Hong Kong-based carriers like Cathay Pacific, which also benefit from the ability to operate flights over Russian airspace. This request underscores the competitive challenges faced by US airlines, which are currently limited in their operations due to the airspace closure.
The situation stems from Russia’s 2022 decision to bar US and other foreign airlines from its airspace following sanctions imposed by the White House and European leaders. In contrast, Chinese airlines were not included in this ban, enabling them to expand their market share by providing more efficient services.
Impact on the US-China Aviation Market
The market between the United States and China is primarily dominated by United Airlines, Delta Air Lines, and American Airlines, all of which are working to rebuild their presence in the region under significant operational restrictions. United Airlines currently operates nonstop flights from San Francisco International Airport (SFO) to Beijing and Shanghai, while Delta Air Lines has recently resumed services from Los Angeles to Shanghai using Airbus A350 jets.
These US airlines are at a disadvantage due to the ongoing restrictions, which force them to take longer routes and incur higher costs compared to their Chinese counterparts. The Department of Transportation has allowed Chinese carriers to operate up to 50 weekly flights since March 2024, raising concerns among US airlines that further expansions should be contingent upon improved competitive conditions.
Chinese airlines have regained significant market share as a result of their ability to overfly Russia. Three major carriers dominate this segment: Air China, China Eastern, and China Southern. These airlines have been able to operate more efficiently, taking advantage of shorter travel times and lower fuel costs, which enhances their appeal to travelers.
Potential Consequences of the Proposed Ban
If the proposed restrictions are enacted, Chinese and potentially Hong Kong carriers could see their flight times increase by two to three hours. This change would likely lead to higher fares and an increased risk of missed connections for passengers. In the short term, capacity might decrease as airlines adjust their schedules, resulting in tighter seat supply and potentially elevated prices on key routes.
While the proposed ban aims to level the playing field for US airlines, it remains uncertain how this will affect overall travel dynamics. An expansion of restrictions to include Cathay Pacific could further complicate the situation, as it would impact one of the region’s most efficient connecting hubs.
Trade groups representing US carriers have expressed support for the proposal, advocating for a balance between capacity and travel demand to ensure fair competition. The overarching concern remains that operations have not returned to a state of normalcy since the closure of Russian airspace, which has drawn parallels to the operational restrictions during the Soviet Union era.
In conclusion, the proposed measures reflect ongoing challenges within the aviation industry due to geopolitical tensions. The resolution to these issues hinges not only on regulatory changes but also on the broader context of international relations and the potential reopening of Russian airspace to all carriers. Until then, US airlines will continue to navigate a complex landscape shaped by operational limitations and competitive pressures.