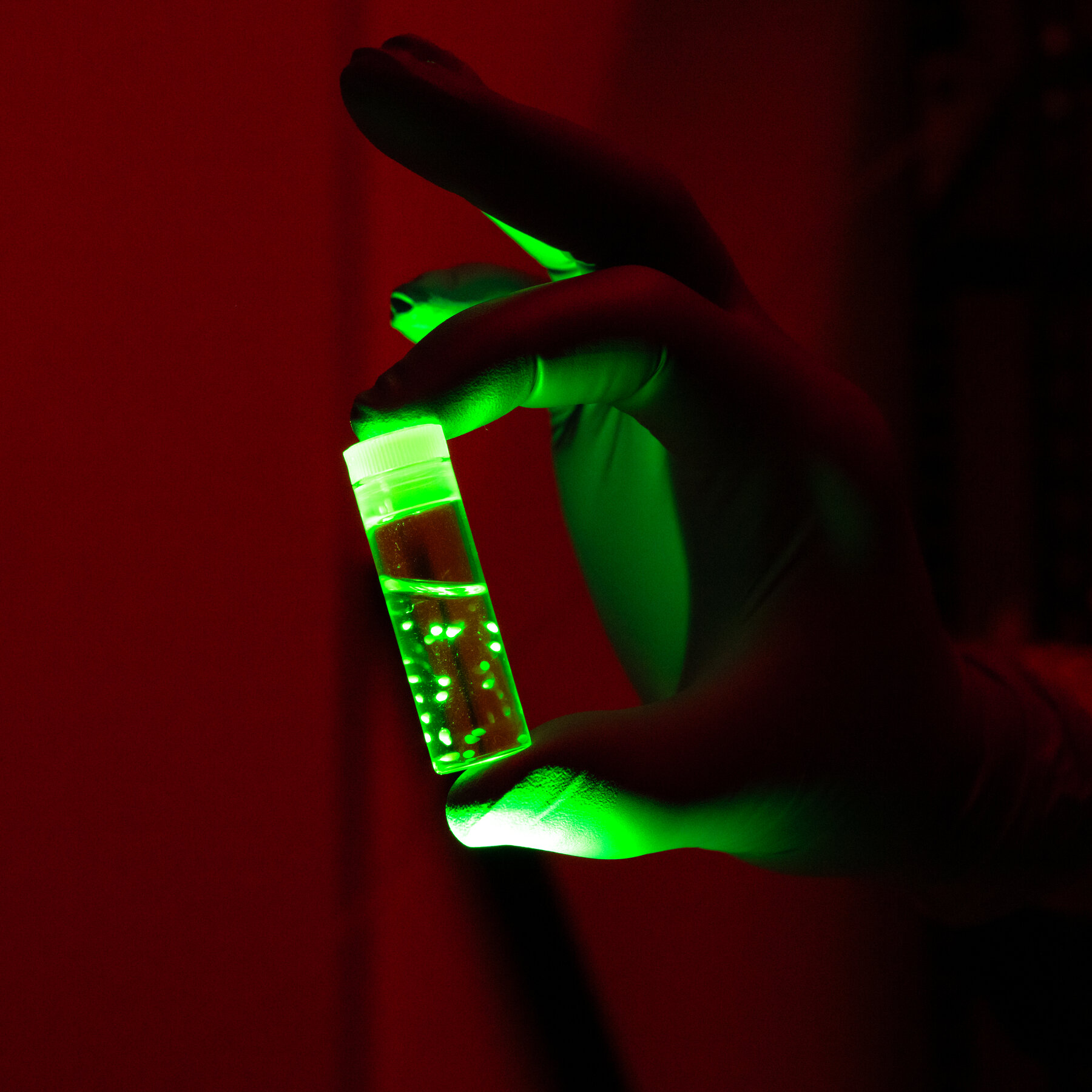
Researchers are making significant strides in understanding fetal brain development and cognitive disorders, such as autism, through the use of lab-grown brain organoids. These miniature, three-dimensional structures mimic key aspects of human brain tissue, offering a unique model for studying complex neurological processes.
The development of brain organoids has been driven by advancements in stem cell technology. Scientists at institutions like Stanford University and the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) have successfully cultivated these organoids from human pluripotent stem cells. By simulating the environment of a developing brain, researchers can observe how neurons form connections and how various factors influence cognitive development.
Utilizing brain organoids allows scientists to explore the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying disorders such as autism. A study published in 2023 by researchers at UCSF demonstrated how these organoids can provide insights into the genetic variations associated with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). The findings revealed differences in neuronal connectivity and growth, shedding light on how these variations may contribute to the condition.
Ethical Considerations Surrounding Brain Organoids
Despite the promising research outcomes, the use of brain organoids raises significant ethical questions. The potential to create models that exhibit human-like properties prompts discussions about the moral implications of manipulating human brain tissue. Critics argue that as organoids become increasingly sophisticated, they may blur the line between artificial and biological intelligence.
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) has initiated guidelines to ensure that research involving brain organoids adheres to ethical standards. Researchers are urged to consider the implications of their work, especially as these models approach the complexity of actual human brains. The ethical debate focuses on issues such as consent, the potential for organoids to develop consciousness, and the long-term effects of such research on society.
In response to these concerns, some scientists advocate for a cautious approach. They emphasize the importance of transparency in research and the need for public engagement to discuss the implications of their findings. Public forums and discussions aim to educate communities about the potential benefits and risks associated with brain organoid research.
Future Directions in Brain Research
As scientists continue to investigate brain organoids, they remain hopeful about the potential applications of this technology. Beyond understanding cognitive disorders, there is growing interest in using brain organoids to test new drugs and therapies. By mimicking human brain responses, these models could lead to more effective treatment options for various neurological conditions.
The future of brain organoid research is poised to revolutionize our understanding of the human brain. With ongoing developments in technology and ethical considerations being addressed, researchers are optimistic about the possibilities that lie ahead. As they navigate the challenges, the ultimate goal remains clear: to enhance our understanding of human brain development and improve the lives of those affected by cognitive disorders.
In conclusion, the exploration of brain organoids represents a significant step forward in neuroscience. While the journey is fraught with ethical dilemmas, the potential benefits to society and medicine are immense, paving the way for groundbreaking discoveries that could transform our understanding of the brain.