URGENT UPDATE: New reports confirm that write amplification is a significant threat to the lifespan of solid-state drives (SSDs). As of today, tech experts are urging users to take immediate action to mitigate this silent killer affecting SSD performance and longevity.
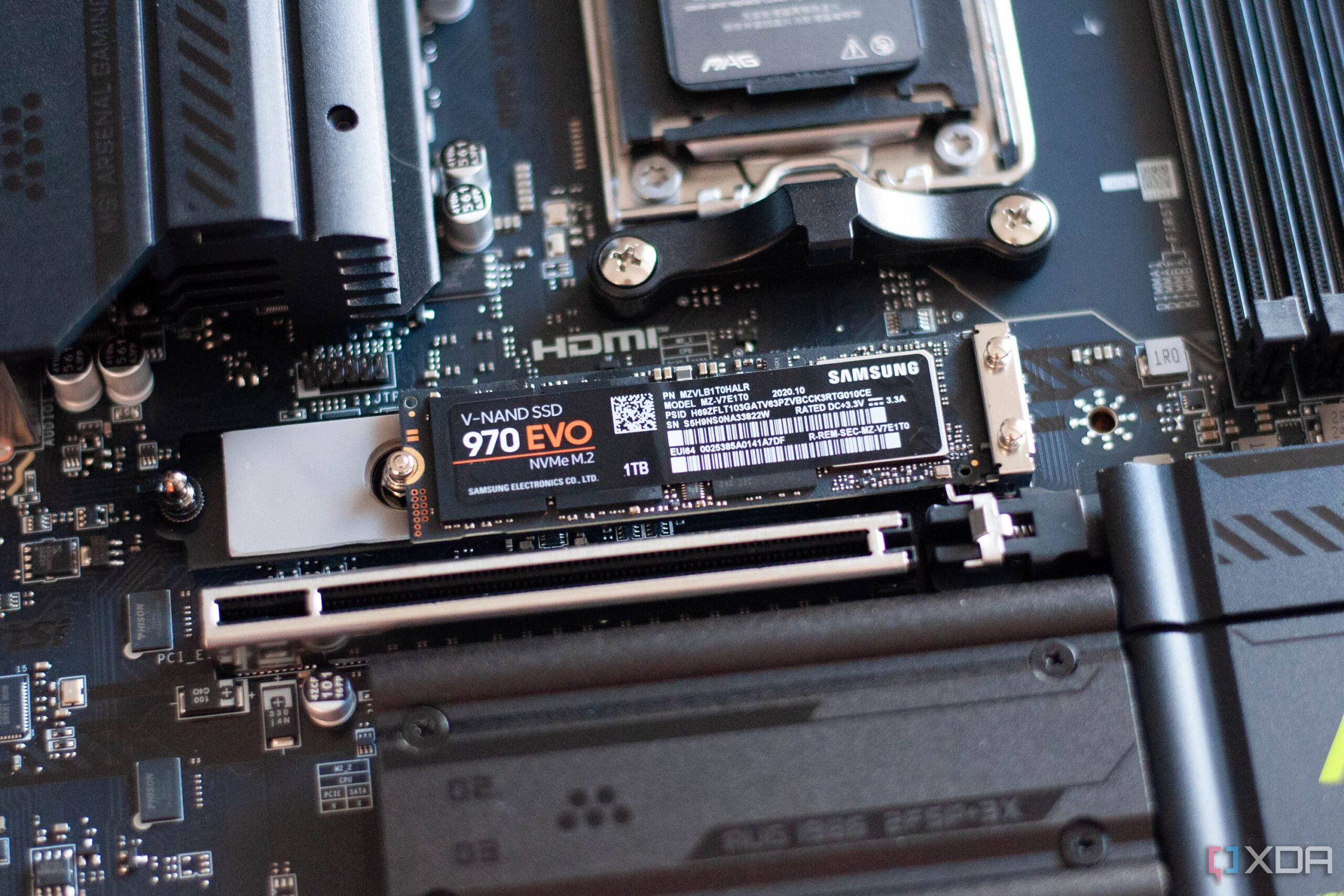
Write amplification occurs when the number of writes to the NAND flash memory in an SSD exceeds the number of writes initiated by the user. This internal issue can lead to a reduced lifespan of your SSD, significantly impacting your device’s performance. Experts report that the ideal write amplification factor (WAF) is 1.0, meaning each write from the computer translates to one write on the SSD. However, older NAND SSDs can have WAFs of 2.5 or higher, resulting in diminished performance and accelerated wear.
Why does this matter RIGHT NOW? As SSDs become the go-to storage option for modern PCs, understanding how to manage write amplification is critical for maintaining peak performance. Failing to do so can lead to premature SSD failure, potentially costing users time and money.
To assess your SSD’s health, you can calculate its write amplification factor using the formula: WAF = NAND Writes / Host Writes. This can be done by checking the drive’s SMART logs, specifically the OCP Cloud Health log parameter at 0xC0. For example, if you write 4GB of files but the drive registers 5GB written, your WAF is 1.25.
How can you fix this pressing issue? Here are several immediate steps you can take:
1. **Maintain Free Space**: Keeping at least 10-20% of your SSD free reduces the frequency of garbage collection operations, which helps mitigate write amplification.
2. **Enable the TRIM Command**: This command allows your operating system to inform the SSD which blocks of data are no longer in use, enhancing garbage collection efficiency.
3. **Consider Active Garbage Collection**: Some SSDs come equipped with this feature to minimize junk data, thereby controlling write amplification.
4. **Invest in DRAM-equipped SSDs**: DRAM helps in page-level mapping, which can reduce write amplification, especially for users with high random write workloads.
Further actions to extend your SSD’s lifespan include keeping the drive cool with adequate cooling solutions or heat sinks, regularly updating your SSD firmware, and minimizing unnecessary writes. Applications that perform extensive random writes should be installed on different drives to preserve the SSD’s health.
As technology rapidly evolves, it’s vital for users to stay informed and proactive about SSD management. Experts emphasize that neglecting these issues could lead to significant performance drops and premature device failure. Take action NOW to ensure your SSD remains in optimal condition, and share this vital information with fellow tech users to help them safeguard their storage devices.