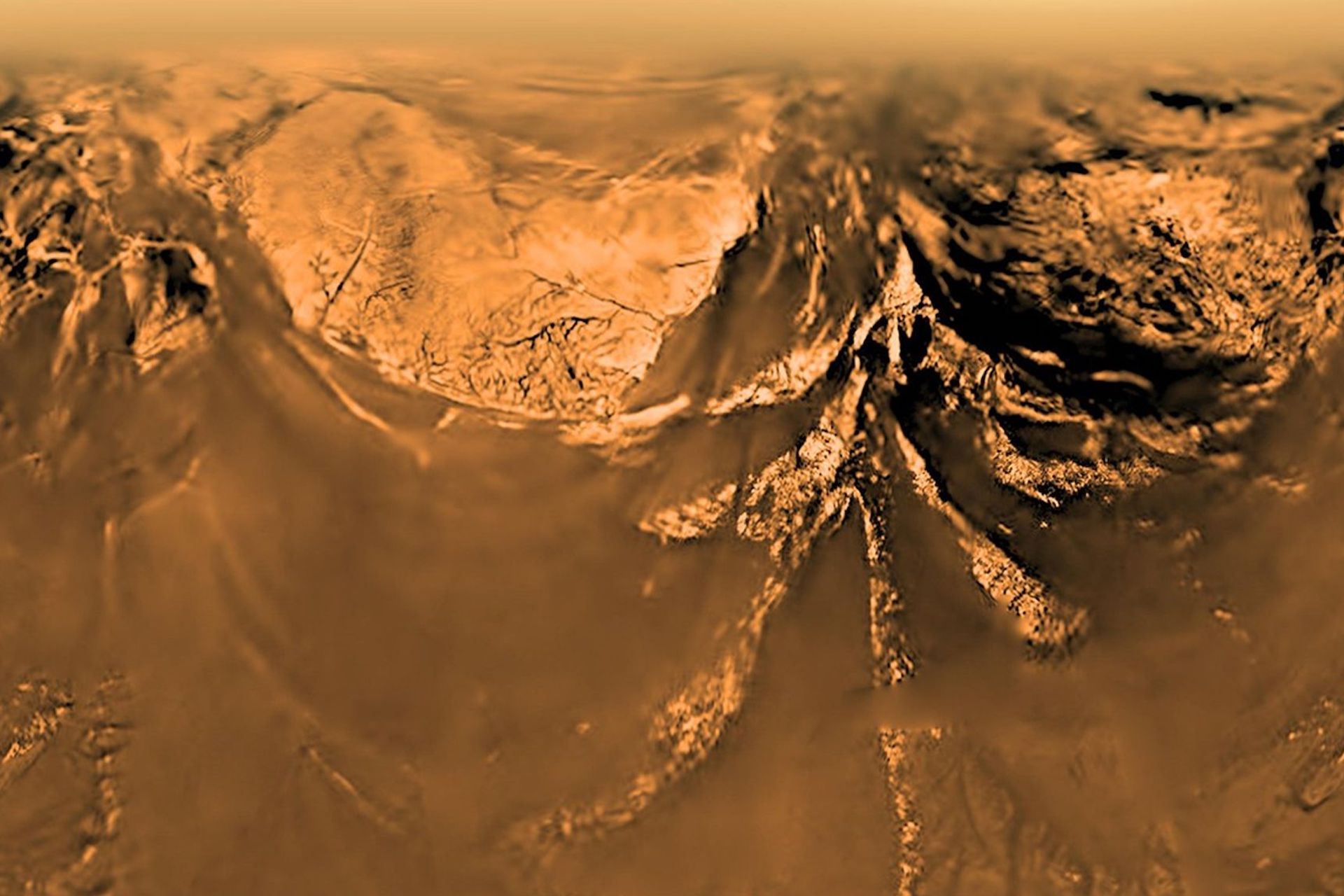
BREAKING: New research from NASA reveals that Titan, Saturn’s largest moon, may have the potential to support life through its methane lakes. A groundbreaking study, published in the International Journal of Astrobiology, highlights the possibility that molecular precursors to life could form in these alien waters, reshaping our understanding of where life might exist beyond Earth.
The implications of this study are enormous. Scientists have long been fascinated by Titan’s unique environment, and this latest revelation opens up a new frontier in the search for extraterrestrial life. The research illustrates how vesicles—tiny, bubble-like structures essential to life—could naturally form in Titan’s methane lakes, providing insights into how life might originate in environments vastly different from our own.
The study is particularly timely as NASA prepares for its Dragonfly mission, set to launch in July 2028. This innovative rotorcraft will explore Titan’s surface, gathering vital data on its atmosphere and geological features. As humanity inches closer to understanding whether life exists beyond our planet, Titan’s methane lakes could serve as a key to unlocking that mystery.
According to Conor Nixon, a researcher at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center and co-author of the study, “The existence of any vesicles on Titan would demonstrate an increase in order and complexity, which are conditions necessary for the origin of life.” This statement underscores the urgency of the research and its potential impact on future space missions.
What makes Titan so intriguing? Unlike Earth, which is rich in water, Titan’s lakes and seas are filled with liquid hydrocarbons, primarily ethane and methane. While these substances are not suitable for swimming, they may hold the key to understanding different forms of life. If vesicles can form in Titan’s lakes, they could replicate the conditions that led to the emergence of living cells on Earth.
The research outlines a fascinating process: vesicles could develop as a result of Titan’s complex meteorological cycles, where methane clouds precipitate as rain, filling river channels and lakes. When these droplets interact with surfaces, they may create double-layered vesicles, competing in an evolutionary process that could lead to the formation of primitive protocells.
As the scientific community eagerly anticipates further exploration of Titan, the findings from this study could significantly alter how we search for life forms in the universe. The potential for life in such hostile conditions challenges our preconceived notions of what constitutes a habitable environment.
Stay tuned for more updates as NASA’s Dragonfly mission approaches, promising to unveil the secrets of Titan and potentially revolutionize our understanding of life’s possibilities beyond Earth. This groundbreaking research is not just an academic exercise; it represents humanity’s quest to discover if we are alone in the universe.