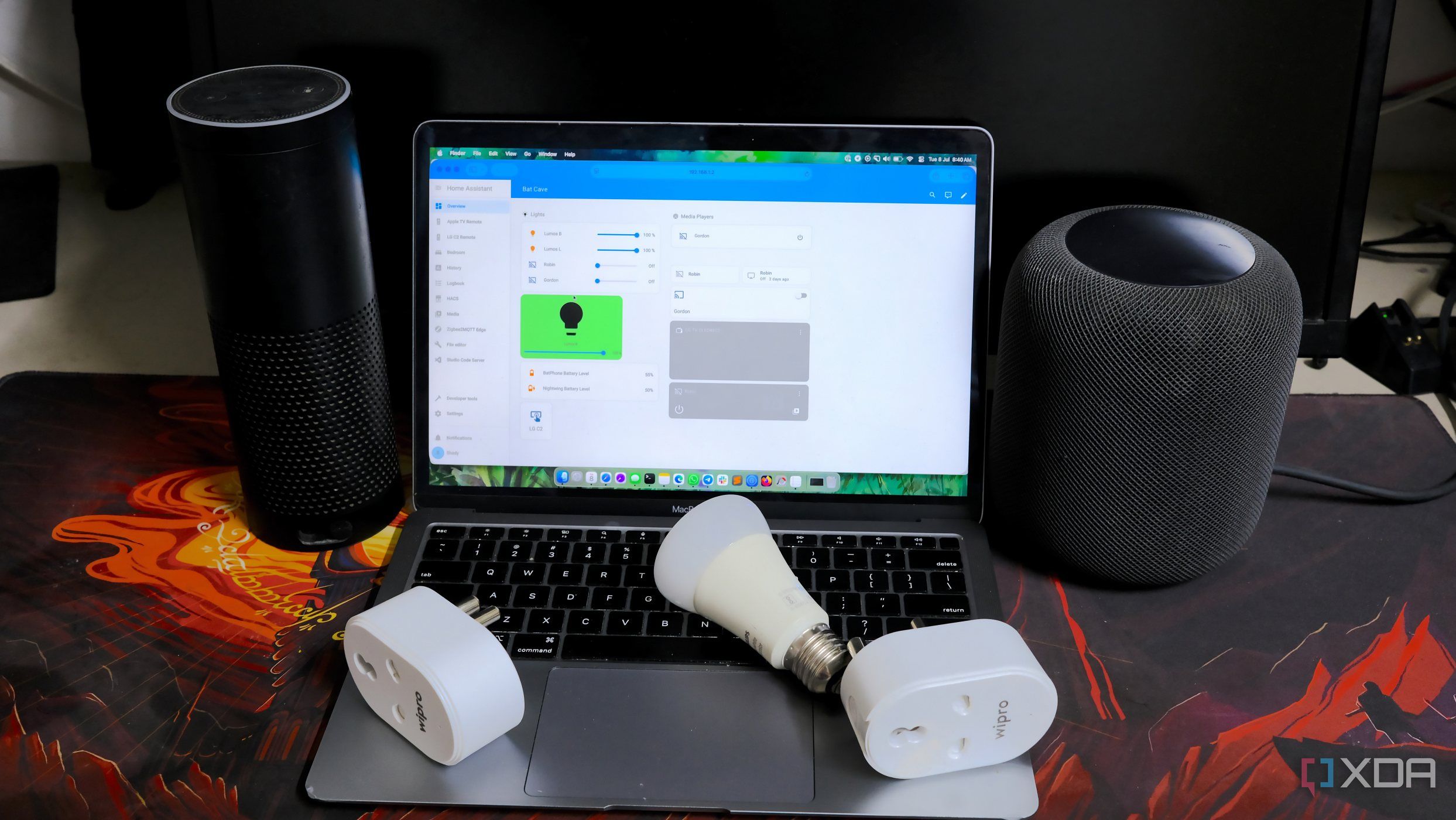
URGENT UPDATE: A growing trend is emerging among smart home enthusiasts as many are abandoning traditional all-in-one IoT hubs in favor of building their own systems with Home Assistant. This shift, gaining momentum in October 2023, highlights the demand for enhanced privacy, local control, and device compatibility.
Smart home users report that while all-in-one hubs appear convenient, they often come with significant limitations. Many users find that these hubs, such as those from Aqara, restrict compatibility to specific vendors and protocols, making them less flexible. For instance, Aqara supports multiple protocols but lacks Z-Wave integration, limiting user options. Frustrated with these constraints, individuals are opting to create customized solutions with Home Assistant, which supports a wider array of devices and protocols.
Developing reports indicate that users are turning to solutions like the Raspberry Pi 4B to run Home Assistant OS, allowing for a more robust and flexible smart home setup. This transition offers users granular control and the ability to operate devices even without an internet connection, a significant advantage over cloud-dependent hubs.
By utilizing Home Assistant, users can pair devices without the restrictions typically imposed by all-in-one hubs. For example, they can easily integrate ESP32-based devices, ensuring that their data remains within their local network and providing complete control over their smart home environment.
Community support for Home Assistant is another compelling reason for this shift. With over 3,300 integrations available, users can access a wealth of resources, including pre-made automations and technical assistance through actively monitored forums. This community-driven model has become invaluable, offering insights and optimizations that enhance the user experience.
The flexibility to choose hardware and software solutions is a significant aspect of the Home Assistant movement. Users appreciate the absence of vendor lock-in, as they can run their systems on various platforms, from Raspberry Pis to virtual machines. This adaptability not only fosters innovation but also lowers costs in the long run.
As more people embrace this DIY approach, the smart home landscape is evolving rapidly. Users report that while the initial setup may require more effort compared to plug-and-play options, the long-term benefits—such as freedom from proprietary restrictions and the ability to customize nearly every aspect—are worth the investment.
In conclusion, the shift towards DIY smart home solutions using Home Assistant is reshaping how users engage with technology. This movement reflects a growing desire for independence, control, and customization in an increasingly connected world. With the rise of this trend, expect to see more innovations and community-driven solutions emerging in the smart home sector.