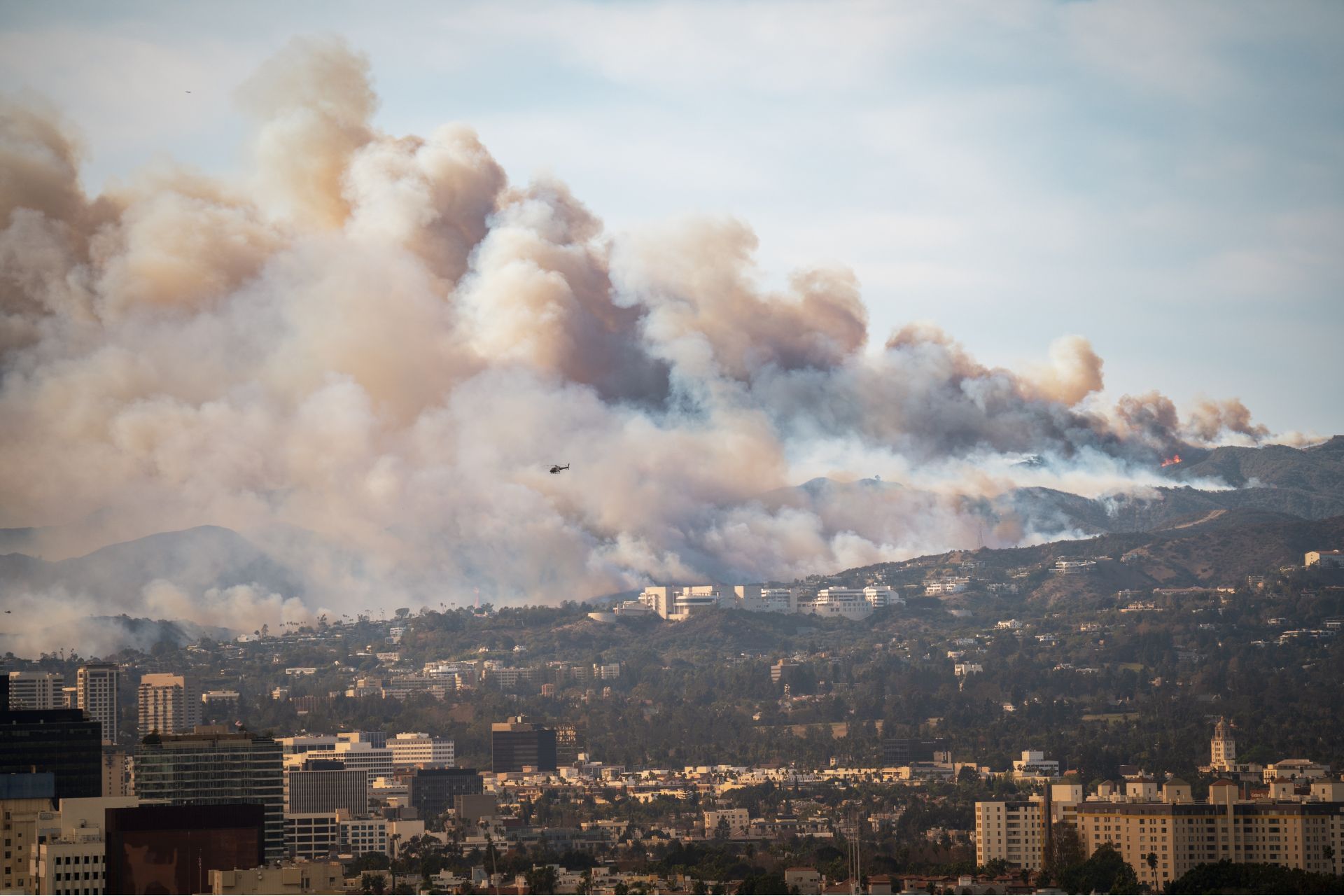
URGENT UPDATE: A shocking new study has revealed that levels of carcinogenic hexavalent chromium (commonly known as chromium-6) in the air over Los Angeles skyrocketed to 200 times greater than baseline levels following the devastating wildfires in January 2023. This alarming finding was confirmed by researchers in late March, more than two months after the flames were extinguished.
The study, shared on the preprint server Research Square and reviewed by the LA Health Consortium, indicates that despite falling below certain safety thresholds, the particles’ unusually small size raises serious health concerns. Lead author Michael Kleeman, an environmental engineer at the University of California Davis, emphasized the urgency of these findings to alert both policymakers and the public.
While the South Coast Air Quality Management District stated there is no immediate health risk based on its own data, the potential for long-term exposure to hexavalent chromium remains troubling. The study identified concentrations ranging from 8.1 to 21.6 nanograms per cubic meter in the most affected neighborhoods, including Altadena and Pacific Palisades. These levels are above the EPA’s indoor limit of 0.1 nanogram per cubic meter but below the workplace exposure limit of 200 nanograms.
The dangers of hexavalent chromium are well-documented, with exposure linked to increased risks of lung, nasal, and sinus cancers, according to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration. Fires can trigger the oxidation of chromium, transforming it into its toxic form, and recent research indicates that it can be present in wildfire smoke and ash.
What is particularly alarming is the size of the particles detected. Kleeman reported that most hexavalent chromium was found in nanoparticles smaller than 56 nanometers. These tiny particles pose a greater health risk as they can penetrate cell membranes and circulate through the bloodstream, reaching vital organs.
Kleeman reassured the public, stating, “The current findings warrant caution, but not panic.” He plans to return to the affected areas to monitor hexavalent chromium levels and identify potential sources of this hazardous pollutant.
As climate change continues to exacerbate wildfire frequency and intensity, the implications of these findings are profound. Kleeman noted, “California is in a new reality where climate change is driving wildfires into major urban areas. We all need to work together to adapt to this new reality.”
Residents of Los Angeles and surrounding areas are urged to remain vigilant and informed about air quality as further studies are conducted. The health impacts of hexavalent chromium are complex and evolving, highlighting the need for community awareness and action in addressing this growing environmental threat.
Stay tuned for further updates as this story develops.