URGENT UPDATE: Users upgrading to 2.5GbE technology are facing unexpected slowdowns, with many reporting speeds that feel the same or are even slower than 1GbE connections. This surprising trend has emerged as tech enthusiasts and everyday consumers alike seek to enhance their network performance.
If you’ve recently upgraded your motherboard, router, or USB adapter to include a 2.5GbE port, you may be left scratching your head as to why your speeds are lacking. The problem lies not within the 2.5GbE port itself, but throughout the network setup. Without a complete overhaul of your network, simply upgrading to a faster LAN port won’t guarantee improved performance.
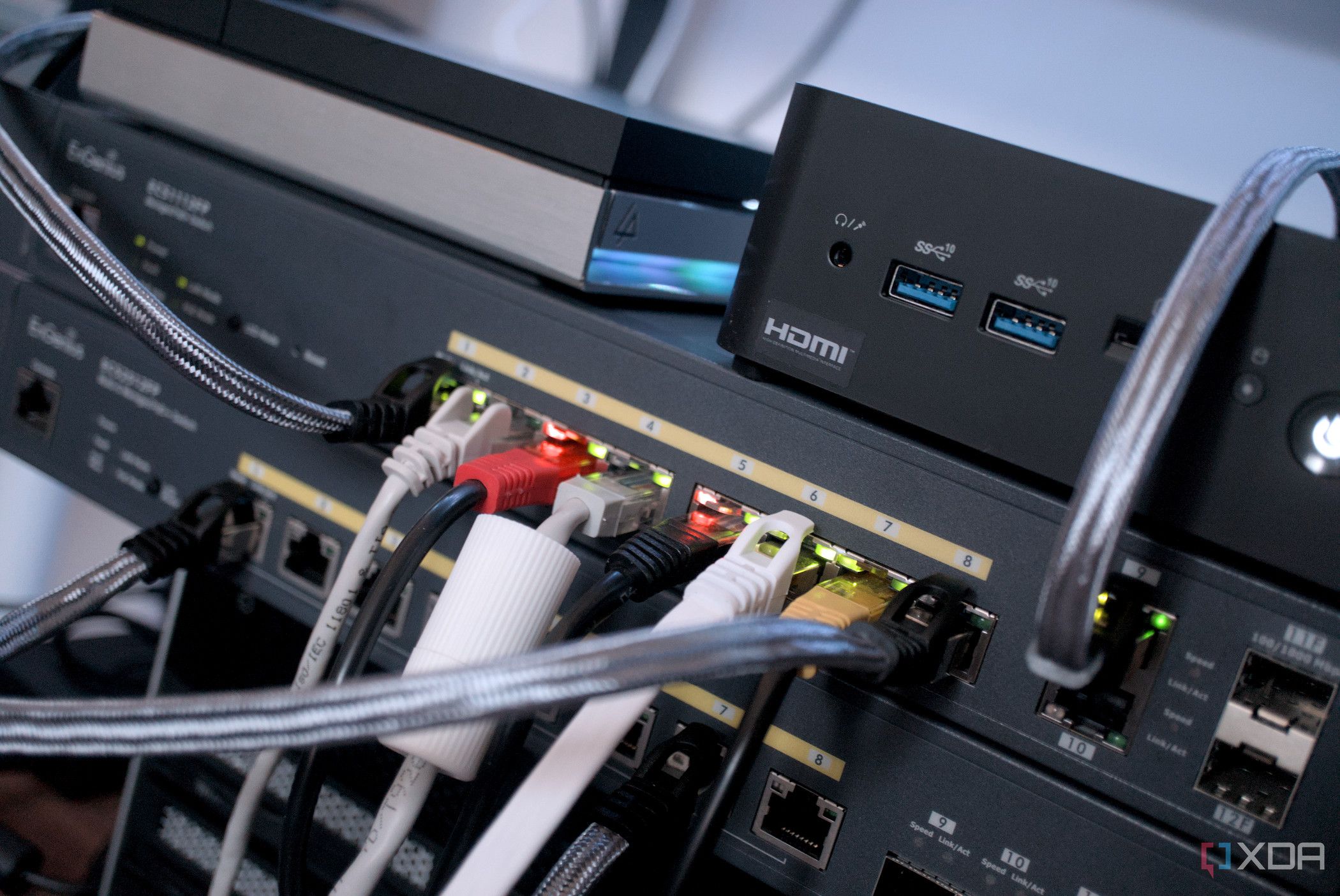
Experts confirm that your connection is only as fast as the weakest link in your setup. This includes your router, network switch, Ethernet cables, storage drives, and the LAN ports on your devices. A single weak element—like a low-quality Cat5e cable—can drastically impede your network’s performance.
Key Reasons for Sluggish Speeds:
1. **Bottlenecked by 1GbE Devices**: The most common issue plaguing users is the presence of a 1GbE device in the network chain. If you connect a 2.5GbE capable PC to a Gigabit switch, your connection speed remains capped at 1GbE. This includes devices like NAS systems, which if limited to 1GbE, will restrict your transfer speeds.
2. **Storage Speed Limitations**: Even if you eliminate the network bottlenecks, your storage can still be a significant limiting factor. Traditional mechanical hard drives often max out around 200MB/s, which is far below the 312.5MB/s theoretical limit of a 2.5GbE connection. Upgrading to SATA SSDs, which can achieve speeds of 500-550MB/s, is essential for maximizing your network’s potential.
3. **Inadequate Ethernet Cables**: Many users underestimate the importance of their Ethernet cables after upgrading. While Cat5e cables can technically support 2.5GbE, not all are built to the same quality. Poorly constructed cables may struggle under higher speeds, leading to silent negotiations down to 1GbE or inconsistent performance. Users should consider upgrading to Cat6 cables, which are available for under $10, to ensure reliable connections.
4. **ISP Limitations**: The disappointment continues when users realize that their internet speed is capped by their Internet Service Provider (ISP). Even with a 2.5GbE setup, if your plan only supports speeds of 300Mbps or 500Mbps, that is the maximum speed you will experience. ISP limitations, alongside factors like network congestion and peak-hour slowdowns, often mean that users do not experience the full benefits of their upgrades.
It’s clear that to truly leverage the advantages of 2.5GbE, users must assess their entire network architecture. This includes ensuring that every component—from cables to storage—can support the desired speed. If one part fails to keep up, the entire network suffers, leaving your 2.5GbE port feeling like just a spec on paper.
As more individuals invest in 2.5GbE technology, it’s crucial to ensure that the entire network is compatible and optimized. Don’t let a single weak link hold you back from achieving faster transfer speeds. Make these adjustments now to experience the benefits that 2.5GbE can offer.
Stay tuned for more updates as this story develops and more solutions emerge to address these pressing network performance challenges.