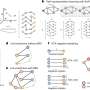
Researchers have unveiled a groundbreaking artificial intelligence (AI) method known as BioPathNet, designed to assist scientists in uncovering hidden connections within extensive biological data networks. This innovative tool enables systematic exploration of complex data, ranging from gene functions and disease mechanisms to potential therapeutic approaches. The development teams from Helmholtz Munich and Mila—Quebec Artificial Intelligence Institute in Montreal, Canada, have detailed their findings in the journal Nature Biomedical Engineering.
BioPathNet addresses a significant challenge in biomedical research: the vast amount of interconnected data within biological networks. Traditional methods often struggle to identify and analyze these intricate relationships effectively. By leveraging advanced AI algorithms, BioPathNet enhances researchers’ ability to navigate through large datasets, revealing insights that may otherwise remain obscured.
The AI tool operates by integrating diverse biological information, allowing for a more comprehensive understanding of how various elements within biological systems interact. Researchers can utilize BioPathNet to pinpoint specific gene functions, elucidate disease mechanisms, and explore new avenues for treatment development. This capability can potentially accelerate the pace of discovery in areas such as personalized medicine and drug development.
The significance of BioPathNet lies not only in its technical capabilities but also in its practical applications. For instance, researchers can use the tool to identify novel drug targets, leading to more effective therapies for various diseases. This advancement could impact the future of healthcare, offering new hope to patients with conditions that currently have limited treatment options.
As the scientific community continues to grapple with the complexities of biological data, tools like BioPathNet provide a promising solution. The collaboration between Helmholtz Munich and Mila exemplifies the importance of interdisciplinary efforts in advancing biotechnology and AI.
With the publication of their findings, the researchers hope to inspire further developments in AI applications within the biomedical field. By fostering a deeper understanding of biological processes, BioPathNet stands to make a lasting impact on research methodologies and therapeutic innovations.
In conclusion, the introduction of BioPathNet marks a significant step forward in the integration of AI into biomedical research. As researchers continue to explore its capabilities, the potential for new discoveries and improvements in patient care grows exponentially. The ongoing collaboration between leading institutions in AI and biomedical research will be crucial in shaping the future of this field.