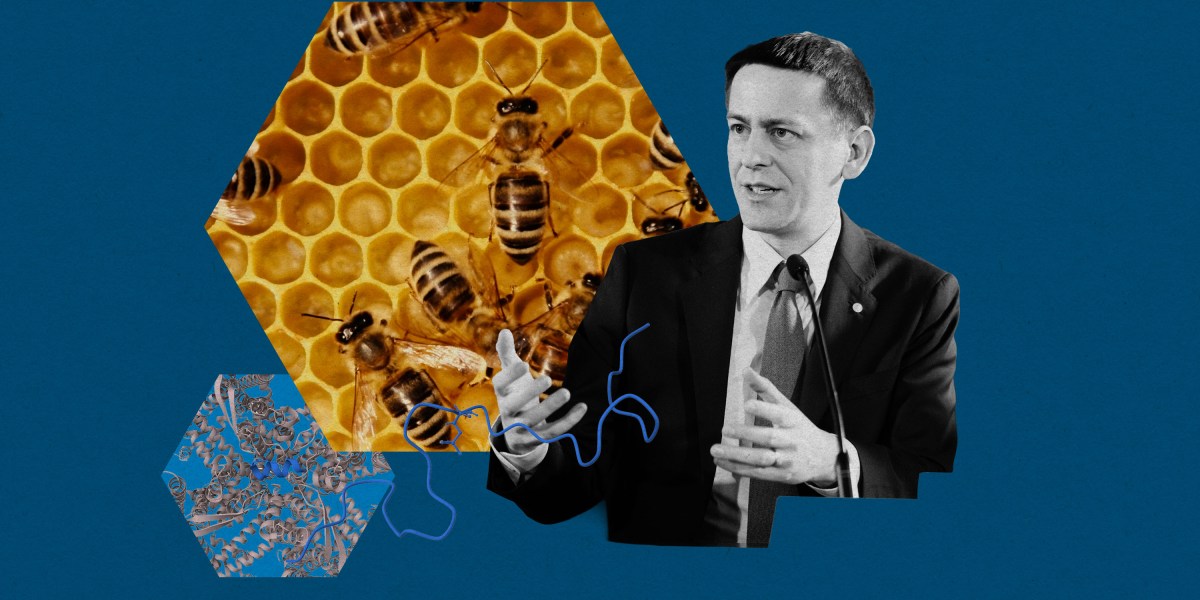
In a significant advancement for protein science, John Jumper and Demis Hassabis have transformed the field with their AI system, AlphaFold. This innovative technology can predict protein structures with atomic precision, dramatically reducing the time required for such analyses from months to mere hours. Jumper and Hassabis were awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2022 for their groundbreaking work, but as the initial excitement wanes, questions arise about AlphaFold’s long-term impact and future applications.
Exploring AlphaFold’s Impact
When Jumper joined Google DeepMind in 2017, he was drawn to a secret project focused on protein structure prediction. Just three years later, AlphaFold 2 emerged, showcasing its ability to achieve lab-level accuracy. This leap has opened new avenues for scientific research, enabling biologists and chemists to explore complex biological questions previously thought insurmountable.
In discussions with Jumper and other scientists, it became clear that AlphaFold has already transformed several areas of research. Scientists are now using the tool to accelerate drug discovery and understand diseases at a molecular level. For example, researchers have utilized AlphaFold to investigate the structure of proteins involved in Alzheimer’s disease, potentially paving the way for novel therapeutic approaches.
Despite the promising applications, Jumper emphasized that AlphaFold is not a complete replacement for experimental methods. While it provides valuable insights, laboratory experimentation remains essential for validating predictions and exploring protein function. As scientists continue to integrate AlphaFold into their workflows, ongoing collaboration between computational and experimental biologists will be crucial for maximizing its potential.
AI Companionship and Privacy Issues
In parallel to advancements in protein science, the rise of generative AI has sparked discussions about privacy, particularly regarding AI companions. A recent study highlighted that many users engage with personalized chatbots on platforms such as Character.AI and Replika for companionship. These AI-driven interactions can mimic relationships with friends, partners, or even therapists, raising important ethical questions about user privacy and data security.
As the popularity of companion AI grows, some state governments are beginning to implement regulations. However, these laws often overlook crucial aspects of user privacy. The lack of comprehensive privacy measures could leave users vulnerable to data misuse, as these platforms collect extensive personal information to create tailored experiences.
Notably, the issue of privacy becomes even more pressing as younger audiences, particularly teenagers, engage with these technologies. Recently, Character.AI announced limitations on the time underage users can spend interacting with its chatbots, aiming to protect young individuals from potential risks associated with excessive reliance on AI companionship.
As discussions about the ethical implications of AI continue, tech companies must prioritize transparency and user safety. The evolving landscape of AI companionship calls for proactive measures to ensure that privacy rights are respected while enabling users to benefit from these innovative technologies.
In summary, while AlphaFold represents a monumental achievement in scientific research, the implications of AI in daily life, particularly concerning privacy, warrant careful consideration. As technology continues to evolve, the balance between innovation and ethical responsibility remains a pivotal challenge for developers and policymakers alike.