This week, the scientific community celebrated remarkable discoveries, from the vastness of the universe to the depths of human history. Researchers unveiled the largest spinning object known, located approximately 140 million light-years away, while studies in southern Africa shed light on a genetically isolated human population. Additionally, significant archaeological finds in China and Greece ignited discussions about ancient civilizations.
Enormous Spinning Structure Found in Space
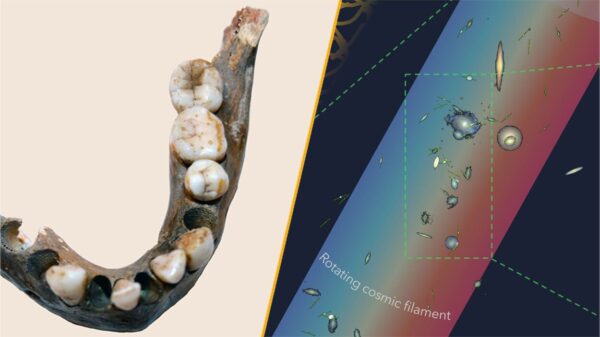
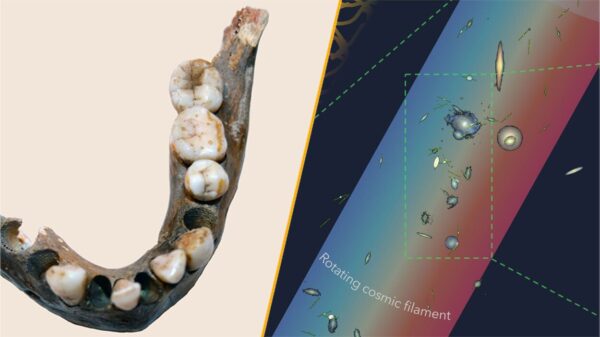
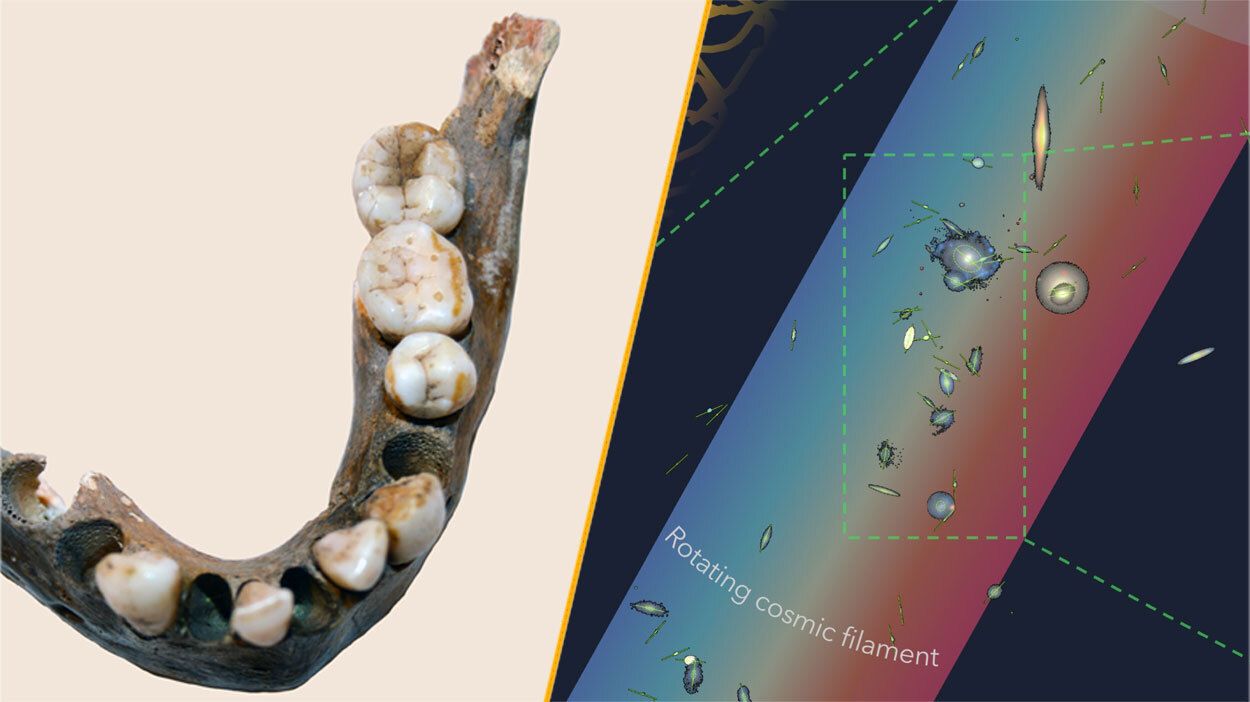
Astronomers have identified the largest spinning structure in the universe, a colossal rotating filament wider than the Milky Way. This discovery is tied to a chain of 14 galaxies and is spinning at roughly 110 kilometers per second (68 miles per second). The remarkable filament was detected through its gravitational influence and its connection to these galaxies, showcasing the intricate web of cosmic relationships.
The implications of this finding are profound, offering insights into galaxy formation and the dynamics of cosmic structures. The research contributes to a growing body of knowledge about the universe’s architecture, reshaping our understanding of its scale and complexity.
Genetic Isolation Revealed in Southern Africa
Closer to home, a study conducted in southern Africa revealed that a human population remained genetically isolated for an astonishing 100,000 years. The research focused on skeletons discovered south of the Limpopo River, which flows from South Africa into Mozambique. The remains, dating back as far as 10,000 years, exhibited a significantly different genetic makeup compared to contemporary humans. The researchers noted that these individuals represent “an extreme end of human genetic variation.”
This groundbreaking study not only enriches our understanding of human evolution but also emphasizes the importance of genetic diversity in adapting to changing environments. The findings could have implications for contemporary studies on human genetics and health.
Puzzling Archaeological Discoveries
In China, archaeologists uncovered a massive pit filled with skulls near a 4,000-year-old city. The find is particularly intriguing as the majority of the skulls belonged to males, diverging from the typical sacrificial patterns observed in similar sites. This discovery raises questions about the social and cultural practices of the civilization that once thrived there.
In Greece, researchers discovered a 2,700-year-old elaborate tomb containing a female skeleton adorned with an upside-down crown. This unusual burial practice further complicates existing narratives about gender roles and societal structures in ancient cultures.
Modern Environmental Challenges
In contemporary news, a large-scale ecosystem project in China, part of the Great Green Wall initiative aimed at combating desertification, has had unintended consequences. Although the tree-planting efforts have succeeded in halting land degradation, they have also altered rainfall and evaporation patterns. A recent analysis indicates that these changes have led to decreased water levels in densely populated regions of the country, highlighting the complexities of environmental interventions.
Additionally, research suggests that the record temperature set in Death Valley in 1913 may have resulted from human error. This revelation adds another layer to our understanding of climate records and the impact of human activity on environmental data.
Innovative Water Extraction Technology
In a significant technological advancement, engineers at MIT have developed a method to extract drinking water from air using ultrasound. This innovative approach can produce water in minutes, greatly surpassing previous evaporation-based systems. The device operates 45 times more efficiently than traditional methods, which rely on sunlight and can take hours or days to yield results.
While the new technology requires a power source, researchers are optimistic about integrating it with solar cells, potentially providing a sustainable solution for water scarcity, particularly in arid regions.
The week’s discoveries not only expand our understanding of the universe and human history but also underscore the ongoing challenges of modern environmental issues and the promise of innovative technologies. As researchers continue to explore these realms, they offer invaluable insights into the past, present, and future of our planet and beyond.