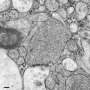
Researchers at Johns Hopkins Medicine have developed an innovative technique known as “zap-and-freeze” to observe communication between brain cells in living tissue. This groundbreaking method allows scientists to visualize previously elusive interactions in both mouse and human brain cells, marking a significant advance in neuroscience.
The zapping involves using a brief electrical pulse to stimulate the brain cells, while the freezing aspect quickly captures the resulting activity, effectively “freezing” the moment for analysis. This dual-action approach enables researchers to monitor cellular communication in real-time, providing insights into how brain cells interact during various functions.
Insights into Cellular Interactions
The findings have the potential to enhance our understanding of numerous neurological conditions. By observing how brain cells communicate, researchers can investigate the mechanisms underlying diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, where communication pathways may become disrupted.
According to the team, this technique not only improves the visibility of cell interactions but also allows for the examination of cellular behavior in its natural environment. Traditional methods often require extensive preparation that can alter the state of the cells, potentially leading to misleading results.
The research highlights the importance of studying living brain tissue, as this is where vital cellular processes occur. The ability to visualize these processes in real-time could revolutionize the approach to neurological research.
Future Applications and Implications
The implications of this technology extend beyond basic research. Understanding brain cell communication can lead to the development of targeted therapies for neurological disorders. As scientists learn more about the interactions at play in healthy versus diseased states, there is potential for creating interventions that could restore normal function.
In a recent statement, the lead researcher emphasized the importance of this technique for future studies, saying, “The zap-and-freeze method provides us with an unprecedented look into the dynamic world of brain cell communication. This could open the door to new therapeutic strategies.”
As this research progresses, the team at Johns Hopkins Medicine plans to conduct further studies to refine the technique and explore its applications across a broader range of neurological conditions. The potential to enhance our understanding of brain functionality could pave the way for advancements in both diagnosis and treatment of various disorders, ultimately benefiting patients worldwide.