A team of scientists has made a significant breakthrough by analyzing lunar samples collected during NASA’s Apollo 17 mission, revealing unexpected sulfur compounds that differ from those found on Earth. This discovery, led by James W. Dottin III, an assistant professor at Brown University, marks a pivotal moment in lunar research, offering insights into the Moon’s geological history and its formation.
Insights from Lunar Samples
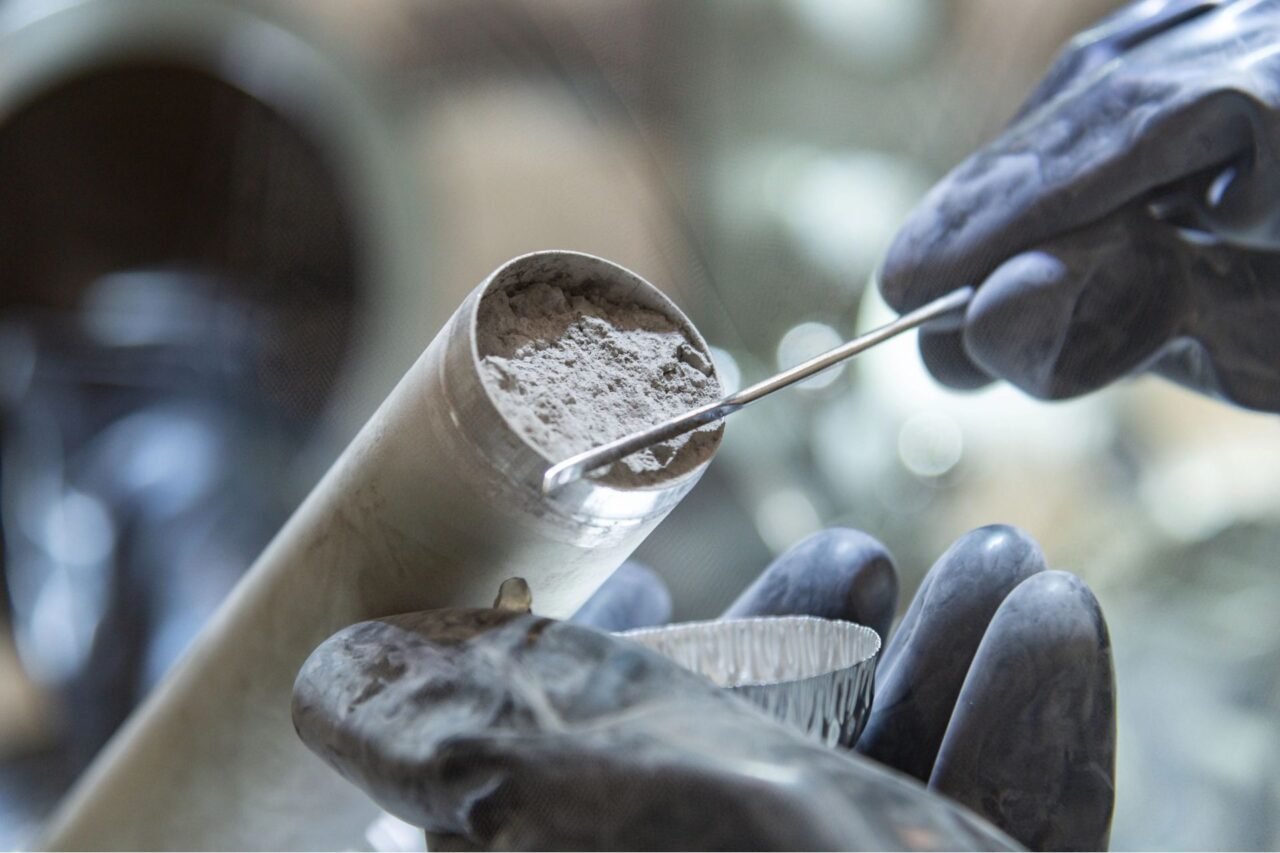
The Apollo 17 mission, which took place in December 1972, was the last time humans set foot on the Moon. During this mission, astronauts returned with over 2,000 samples of lunar rock and dust, some of which were preserved for future research. Recently, NASA initiated the Apollo Next Generation Sample Analysis (ANGSA) program, allowing new scientific proposals to study these samples. Dottin’s research, published in JGR Planets, focused on sulfur isotopes within samples extracted from the Moon’s Taurus-Littrow valley.
Utilizing advanced techniques such as secondary ion mass spectrometry, which was not available at the time of the original sample collection, Dottin and his team measured the sulfur isotopes to reveal distinct isotopic fingerprints. Their findings indicate that the sulfur compounds in the lunar samples possess significantly lower levels of sulfur-33, a stable isotope, compared to those found on Earth.
Revolutionizing Lunar Geology
Dottin expressed his surprise at the results, stating, “My first thought was, ‘Holy shmolies, that can’t be right.’” After thorough verification, the team confirmed that their findings were indeed accurate. The low levels of sulfur-33 suggest that the sulfur may have originated from chemical reactions during the Moon’s early history or from its formation processes.
Current scientific consensus posits that the Moon formed from debris resulting from a colossal impact involving Earth and a Mars-sized body known as Theia. The isotopic differences observed could indicate the presence of Theia’s sulfur signature within the Moon’s mantle, providing new clues about the formative events of our solar system.
As researchers expand their studies to include sulfur isotopes from other celestial bodies, including Mars, Dottin anticipates that these investigations will further illuminate the historical connections between Earth and its natural satellite. The isotopic analysis conducted in this study not only enhances our understanding of lunar geology but also contributes to the broader narrative of how planetary bodies within our solar system formed and evolved over billions of years.
This research underscores the importance of continued exploration and study of lunar materials, as they hold vital information about the origins of both the Moon and Earth. With this new knowledge, scientists are better equipped to unravel the mysteries of our solar system’s history, paving the way for future discoveries.