A significant breakthrough in kidney research has revealed a critical “pressure sensor” within the kidney that plays a vital role in regulating blood pressure and fluid levels in the body. This discovery, announced in a study published in early 2023, sheds light on the long-observed phenomenon of how kidneys detect changes in blood volume—something that has puzzled scientists for decades without a clear mechanistic explanation.
Understanding the mechanisms behind kidney function is essential for managing various health conditions, including hypertension and fluid imbalance. The newly identified sensor enables the kidneys to sense fluctuations in blood volume, which is crucial for maintaining homeostasis.
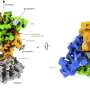
Researchers at a prestigious institution conducted the study, employing advanced techniques to pinpoint the exact location and function of this pressure sensor. The sensor’s ability to respond to changes in blood flow and pressure is integral to the kidneys’ role in fluid regulation.
Implications for Health and Medicine
The implications of this discovery are vast. By providing insight into how the kidneys operate, medical professionals may develop better treatment strategies for patients suffering from high blood pressure or fluid retention. Currently, these conditions affect millions globally, making the identification of such a sensor a potentially transformative finding in nephrology.
Dr. Jane Thompson, a leading researcher on the project, emphasized the importance of the study, stating, “Understanding the kidney’s mechanisms for sensing pressure could lead to innovative therapies that improve patient outcomes.” Her team’s work is expected to pave the way for future research exploring how this sensor can be targeted in clinical settings.
Moreover, this discovery opens up avenues for further investigations into other kidney functions and their relationship with systemic health. As researchers continue to explore the intricacies of kidney biology, they hope to uncover additional sensors or pathways that may influence kidney function and overall health.
In conclusion, the identification of the kidney’s pressure sensor marks a significant advancement in our understanding of fluid balance and blood pressure regulation. This research not only enhances our knowledge of kidney function but also holds promise for improving medical interventions for related health issues. As studies progress, the potential for new therapeutic approaches continues to grow, offering hope to those affected by kidney-related conditions.