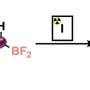
A significant advancement in drug development has emerged from the University of Gothenburg, where researchers have created stable boron-fluorine compounds. This breakthrough allows for enhancing a drug’s effects or minimizing side effects without compromising the integrity of the medicine. The findings, published in the journal Angewandte Chemie International Edition, hold promise for the pharmaceutical industry.
The newly developed compounds offer a solution to a common challenge in drug formulation. Traditional compounds often break down during the development process, which can lead to diminished efficacy or increased adverse effects. By utilizing these stable boron-fluorine compounds, scientists can maintain the desired properties of medications while optimizing their performance.
Implications for Drug Development
This innovative approach has the potential to streamline the drug development process significantly. Researchers have long sought ways to enhance the therapeutic effects of drugs while reducing their side effects. The stability of boron-fluorine compounds allows for greater flexibility in modifying drug formulations. This flexibility can lead to faster development times and reduced costs in bringing new medications to market.
According to the study, these compounds can be integrated into various pharmaceutical formulations, paving the way for more efficient drug design. The ability to maintain stability while making necessary adjustments means that pharmaceutical companies could potentially save millions in research and development costs.
The researchers emphasized that this work could lead to new treatments for a variety of illnesses, potentially improving patient outcomes. With the pharmaceutical industry continually searching for ways to enhance drug efficacy and safety, these developments could represent a significant leap forward.
Future Research Directions
Looking ahead, further research is necessary to explore the full range of applications for these stable boron-fluorine compounds. The team at the University of Gothenburg is planning to investigate their use in specific therapeutic areas, which may include oncology and chronic diseases.
As the scientific community assesses the impact of these compounds, the potential for collaboration with pharmaceutical companies could lead to practical applications that benefit patients worldwide. The researchers are optimistic that their discoveries will influence future drug development practices, ultimately contributing to more effective and safer treatments.
In conclusion, the development of stable boron-fluorine compounds at the University of Gothenburg represents a promising advancement in the field of drug design. By addressing the critical challenges of drug stability and efficacy, this research may pave the way for innovative therapeutic solutions that can improve health outcomes on a global scale.