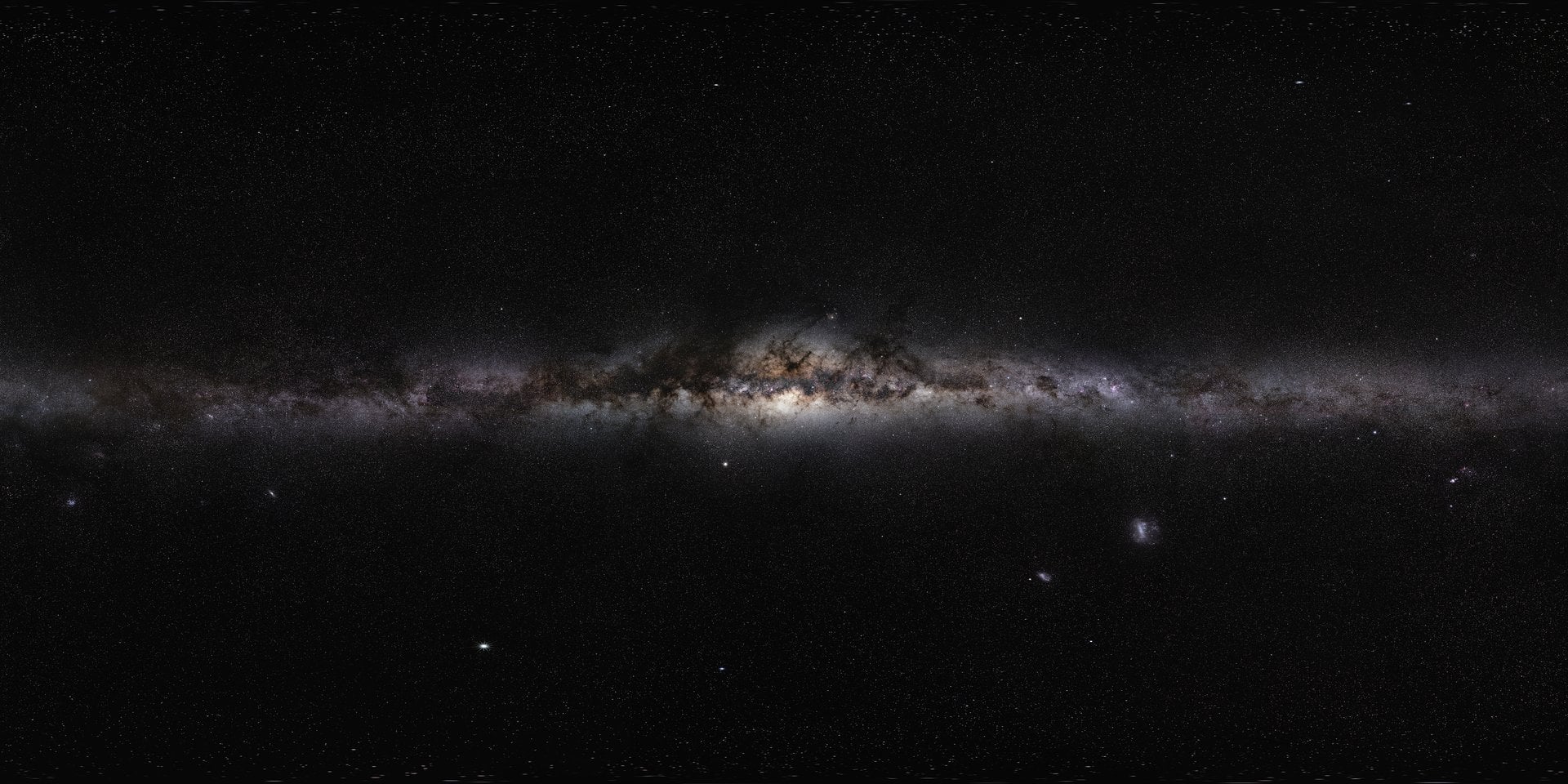
A collaborative team of researchers from the RIKEN Center for Interdisciplinary Theoretical and Mathematical Sciences (iTHEMS) in Japan, alongside colleagues from the University of Tokyo and the Universitat de Barcelona, has achieved a significant breakthrough in astrophysics. They recently completed the world’s first comprehensive simulations of the Milky Way, accurately representing over 100 billion stars over a period of 10,000 years. This monumental effort not only models a hundred times more stars than previous simulations but does so at a speed that is also one hundred times faster.
The innovative simulation was made possible by leveraging 7 million CPU cores, advanced machine learning algorithms, and sophisticated numerical simulations. The findings were detailed in a paper titled “The First Star-by-star N-body/Hydrodynamics Simulation of Our Galaxy Coupling with a Surrogate Model,” published in the *Proceedings of the International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis* (SC ’25).
Advancements in Galactic Modeling
Creating simulations that capture the dynamics of individual stars is crucial for verifying theories of galactic formation, structure, and evolution. Historically, astronomers faced significant challenges in achieving satisfactory complexity due to the numerous forces at play, including gravity, fluid dynamics, supernovae, and the effects of supermassive black holes (SMBHs). Until now, the computational power required to model such complex systems was lacking. Existing models were capped at approximately one billion solar masses, representing less than 1% of the stars in the Milky Way.
Currently, simulations of galactic evolution take a considerable amount of time on state-of-the-art supercomputing systems. For instance, simulating just one million years of galactic evolution could require about 315 hours, or over thirteen days, which accounts for only 0.00007% of the Milky Way’s 13.61 billion-year age. To simulate an entire billion years would take over 36 years with current technologies, limiting astronomers to studying only large-scale events.
To overcome these limitations, the team, led by researcher Hirashima, implemented a machine learning surrogate model that optimizes resource usage. This AI-driven approach was trained on high-resolution supernova simulations, allowing it to predict the impact of these explosive events on surrounding gas and dust up to 100,000 years post-explosion. By integrating this AI model with physical simulations, the researchers successfully modeled the dynamics of a Milky Way-sized galaxy alongside small-scale stellar phenomena.
Significant Findings and Future Implications
Testing on the Fugaku and Miyabi Supercomputer Systems at RIKEN and the University of Tokyo validated the model’s effectiveness. The results indicated that the new method could simulate star resolution in galaxies containing over 100 billion stars, completing 1 million years of evolution in just 2.78 hours. This efficiency means that a full billion years of galactic history could potentially be simulated in just 115 days.
These advancements provide astronomers with a powerful tool for exploring theories regarding galactic evolution and the origins of the universe. Furthermore, they demonstrate the potential of incorporating surrogate AI models to enhance complex simulations, reducing both the time and energy demands of such computationally intensive tasks.
The implications of this research extend beyond astrophysics. The AI shortcut methodology could also facilitate complex simulations in other fields, such as meteorology, ocean dynamics, and climate science. This innovative approach marks a significant step forward in our understanding of not only the Milky Way but also the broader cosmos.