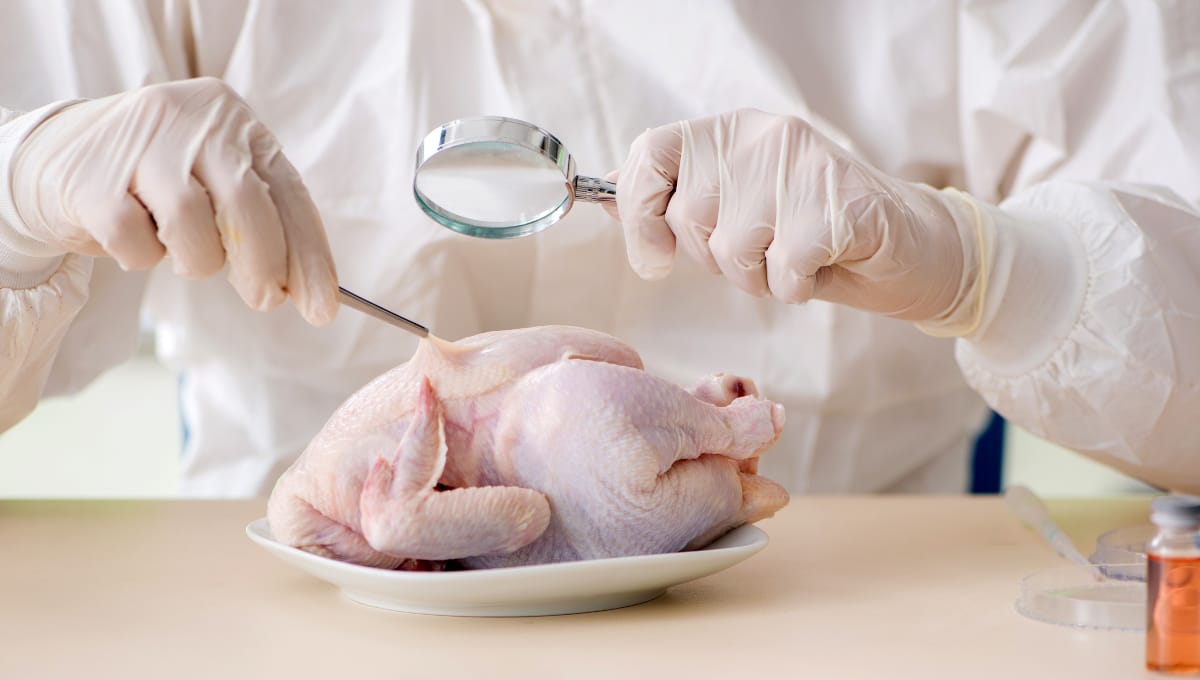
Recent research has identified chicken as the primary source of Salmonella infections in the United States, accounting for over one-third of reported cases. This finding underscores a significant public health concern regarding food safety, particularly in poultry products.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Salmonella causes approximately 1.35 million infections, 26,500 hospitalizations, and 420 deaths in the United States annually. The new study highlights that chicken, often consumed in various forms, is linked to an alarming percentage of these infections.
Understanding the Impact of Salmonella
Salmonella is a bacterium that can cause gastrointestinal illness, leading to symptoms such as diarrhea, fever, and abdominal cramps. While it can be found in a variety of foods, chicken has emerged as a significant contributor to these health risks. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has been actively working to reduce Salmonella contamination in poultry, yet the prevalence remains troubling.
The study, conducted by researchers from several institutions, analyzed data from multiple sources, including health departments and food safety agencies. It revealed that improper handling and cooking of chicken are major factors in the spread of Salmonella. The report advocates for increased awareness and education about safe food practices among consumers and food handlers.
Recommendations for Consumers
To mitigate the risks associated with Salmonella, experts recommend several key practices when handling and cooking chicken. It is essential to cook chicken to an internal temperature of at least 75 degrees Celsius (165 degrees Fahrenheit) to effectively kill harmful bacteria. Additionally, avoiding cross-contamination with other foods, using separate cutting boards, and washing hands frequently can significantly reduce infection risks.
The National Chicken Council emphasizes the importance of proper cooking methods and food safety practices. They are collaborating with health agencies to promote consumer education initiatives aimed at reducing the incidence of Salmonella infections.
This research serves as a call to action for both consumers and industry stakeholders. As chicken remains a staple protein source for many households, understanding the risks and implementing effective safety measures is critical in preventing foodborne illnesses. Continued vigilance and education will be necessary to combat the ongoing challenges posed by Salmonella in poultry.