A research team from the University of Melbourne has developed a groundbreaking deep learning framework named Themeda that significantly enhances the prediction of land cover changes, particularly in savanna ecosystems. Published in the Journal of Remote Sensing on September 11, 2025, this innovative model integrates advanced neural network architectures with extensive satellite data to forecast future land cover dynamics across northern Australia.
Land cover changes have far-reaching impacts on erosion, water quality, fire regimes, and species habitats. Despite advances in remote sensing technology, accurately predicting these shifts remains a complex challenge. Savannas, which cover one-sixth of the Earth’s land surface, are particularly difficult to model due to their seasonal rainfall patterns, frequent fires, and diverse vegetation types. Themeda aims to address these challenges through a comprehensive approach that combines multiple environmental factors.
Innovative Methodology Enhances Predictive Accuracy
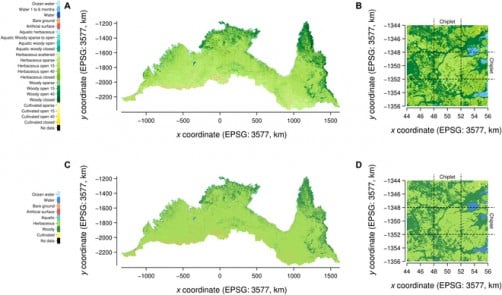
The framework employs both ConvLSTM and a novel Temporal U-Net design to process spatiotemporal data across multiple scales. By integrating 23 land cover classes with environmental predictors such as rainfall, maximum temperature, fire scars, soil fertility, and elevation, Themeda utilizes 33 years of satellite-derived data (from 1988 to 2020) to achieve remarkable accuracy in its predictions. In validation tests, the model reached an impressive 93.4% accuracy rate for FAO Level 3 categories, surpassing the persistence baseline of 88.3%.
Additionally, the model demonstrated a nearly tenfold reduction in prediction errors at regional scales, achieving a Kullback–Leibler divergence as low as 1.65 × 10−3. The ablation experiments indicated that rainfall is the most significant predictor, followed by temperature and late-season fire scars. Notably, Themeda proved capable of generalizing well to previously unseen years and spatial regions, although extreme climatic conditions, such as the exceptionally hot and dry 2019 season, posed challenges to its accuracy.
Practical Applications for Land Management
The potential applications of Themeda extend beyond academic research. The model’s probabilistic outputs provide pixel-level classifications and landscape-scale insights, making it suitable for integration into hydrological, fire, and biodiversity risk models. This predictive capability supports proactive land management strategies, allowing communities and policymakers to anticipate ecological risks rather than merely reacting to them.
Lead author Robert Turnbull emphasized the transformative nature of their findings: “Our findings show that deep learning can move beyond static mapping toward dynamic forecasting of ecosystems. By learning from decades of environmental data, Themeda provides predictions that are not only accurate but also transparent about uncertainty. This opens new possibilities for proactive land management, helping communities and policymakers anticipate ecological risks rather than reacting after the fact.”
Furthermore, the framework can assist in erosion control, hydrological modeling, and fire management strategies, including early-season burning programs that reduce wildfire intensity and carbon emissions. By forecasting vegetation shifts, Themeda can inform national carbon accounting and ecosystem restoration initiatives, thereby addressing critical challenges related to food security, biodiversity loss, and sustainable resource use.
In naming the framework after Themeda triandra (commonly known as kangaroo grass), the research underscores both the ecological and cultural significance of this species, while showcasing the scalability of AI for environmental forecasting.
The development of Themeda represents a pivotal advancement in integrating AI-driven ecological forecasting into real-world decision-making. As climate extremes continue to intensify, such predictive capacity will be essential for safeguarding biodiversity and sustaining livelihoods in vulnerable regions like Australia’s savannas.
This research received support from the University of Melbourne’s Research Computing Services and the Petascale Campus Initiative, with resources provided by the National Computational Infrastructure (NCI), backed by the Australian Government. The study also acknowledges the contributions from the University of Melbourne Wildfire Futures Hallmark Research Initiative, Melbourne Climate Futures, and the Melbourne Centre for Data Science.