Scientists may have made a breakthrough in the search for dark matter, a mysterious substance that has eluded direct detection for nearly a century. Using data from NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope, researchers suggest they have observed potential evidence of dark matter, providing a clearer understanding of the universe’s hidden components.
Historical Context and Initial Discoveries
The concept of dark matter originated in the early 1930s when Swiss astronomer Fritz Zwicky studied the movement of galaxies within the Coma Cluster. He noted that the galaxies were moving at speeds that could not be explained by their visible mass alone. Zwicky proposed the existence of an unseen form of matter, which he termed “dark matter,” as a means to explain the discrepancy.
For decades, the existence of dark matter remained a theoretical concept, supported by indirect evidence such as gravitational effects on visible matter and the cosmic microwave background radiation. Despite extensive research and numerous hypotheses, direct detection of dark matter had not been achieved.
Recent Findings from NASA’s Fermi Telescope
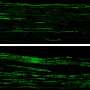
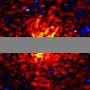
In a significant advancement, scientists utilizing data from the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope have reportedly identified signals that could be attributed to dark matter interactions. This revelation marks a potential turning point in astrophysics, as it could provide the first direct evidence of dark matter’s existence.
The Fermi Telescope, launched in 2008, has been instrumental in studying high-energy phenomena in the universe. Its ability to detect gamma rays allows scientists to explore cosmic events and conditions that were previously beyond reach. The recent findings indicate that certain gamma-ray emissions may be linked to dark matter particles, suggesting that the elusive substance might finally be “seen.”
While the full implications of this discovery are still under investigation, researchers are optimistic. The potential identification of dark matter could reshape our understanding of the universe, influencing theories related to galaxy formation and cosmic evolution.
As the scientific community continues to analyze these findings, the prospect of unraveling the mysteries surrounding dark matter brings renewed excitement and curiosity. The implications could lead to new technologies and deeper insights into the fabric of the cosmos.
This discovery not only pays homage to the pioneering work of figures like Zwicky but also highlights the ongoing quest for knowledge in the field of astrophysics. With this latest development, the future of dark matter research appears promising, offering the potential for transformative advancements in our understanding of the universe.