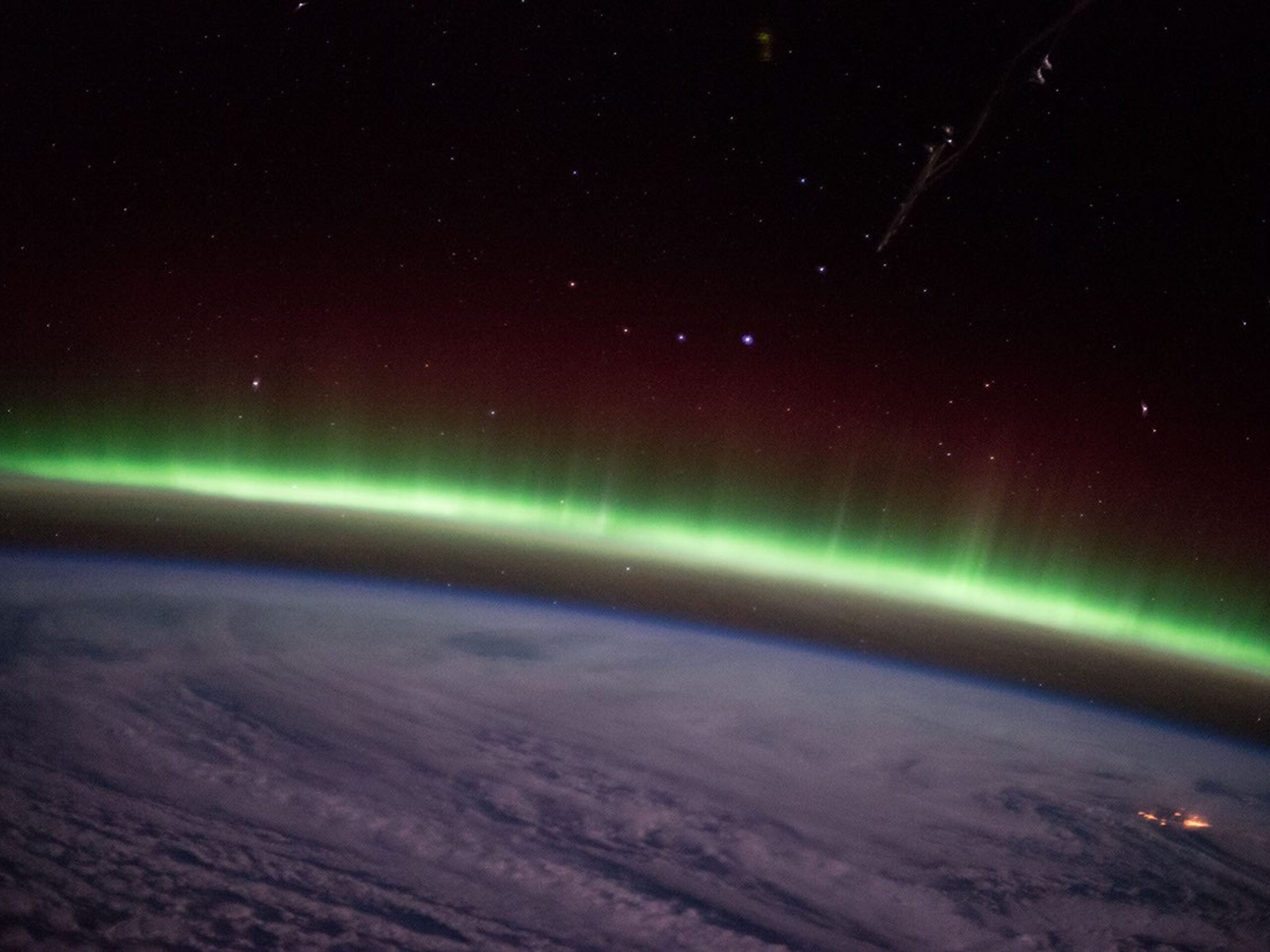
NASA scientists have made a significant breakthrough in understanding the mechanisms that power a specific type of aurora. Their findings, published in the journal Nature Communications on March 14, 2024, reveal the intricate relationship between solar wind and the formation of auroras, particularly over Earth’s polar regions.
The research focuses on the way charged particles from the sun interact with Earth’s magnetic field. When these particles collide with gases in the atmosphere, they produce stunning light displays known as auroras. The study provides new insights into how variations in solar activity can amplify these natural phenomena.
Key Findings on Aurora Mechanics
The team of researchers analyzed data collected from NASA’s Polar Orbiting Satellites and other observational platforms. They discovered that certain types of auroras, particularly the more intense ones, are driven by specific conditions in the solar wind. This interaction leads to heightened electromagnetic activity in the Earth’s magnetosphere, resulting in brighter and more dynamic auroras.
Lead author Dr. Emily Harris, a physicist at NASA, emphasized the importance of these findings. “Understanding the precise conditions that lead to stronger auroral displays helps us better predict their occurrences,” she stated. “This knowledge not only enriches our scientific understanding but also enhances our ability to protect satellites and other technologies from solar storms.”
The research underscores the vital role that solar wind plays in shaping auroral activity. Variations in solar wind speed and density can significantly influence the intensity of auroras. When the solar wind is stronger, it can lead to more spectacular light shows, captivating observers in locations like Alaska and Norway.
Implications for Future Research
These findings open new avenues for further research into the relationship between solar activity and Earth’s atmospheric phenomena. Scientists are now looking to develop predictive models that can forecast auroras based on solar wind conditions. This could prove essential for both scientific inquiry and practical applications, such as improving satellite operations and communication systems affected by solar activity.
Additionally, the study highlights the interconnectedness of our solar system. Understanding how solar activity influences atmospheric phenomena on Earth can provide insights into similar processes on other planets, enhancing our knowledge of planetary science.
NASA continues to prioritize research on solar phenomena, as these studies have significant implications for space weather forecasting and the protection of our technological infrastructure. The agency is committed to advancing our understanding of the dynamic processes at play in our solar system and their effects on Earth.
As scientists delve deeper into the complexities of auroras, the awe-inspiring displays in the night sky serve as a reminder of the intricate dance between our planet and the sun. This research not only satisfies human curiosity but also has practical implications for life on Earth.