The potential for seasonal briny water on the Martian surface has emerged as a significant focus in astrobiology research. A recent study led by Vincent Chevrier, an associate research professor at the University of Arkansas, presents compelling evidence suggesting that these briny patches could form under specific conditions on Mars.
This exploration builds on earlier missions, particularly the Viking 1 and Viking 2 missions in 1976, which were among the first to analyze Martian soil for signs of organic molecules and biological processes, known as biosignatures. Although initial findings were inconclusive and fostered skepticism about past life on Mars, the discovery of geological features indicative of flowing water renewed interest in the planet’s potential to host life.
Seasonal Frosts and Brine Formation
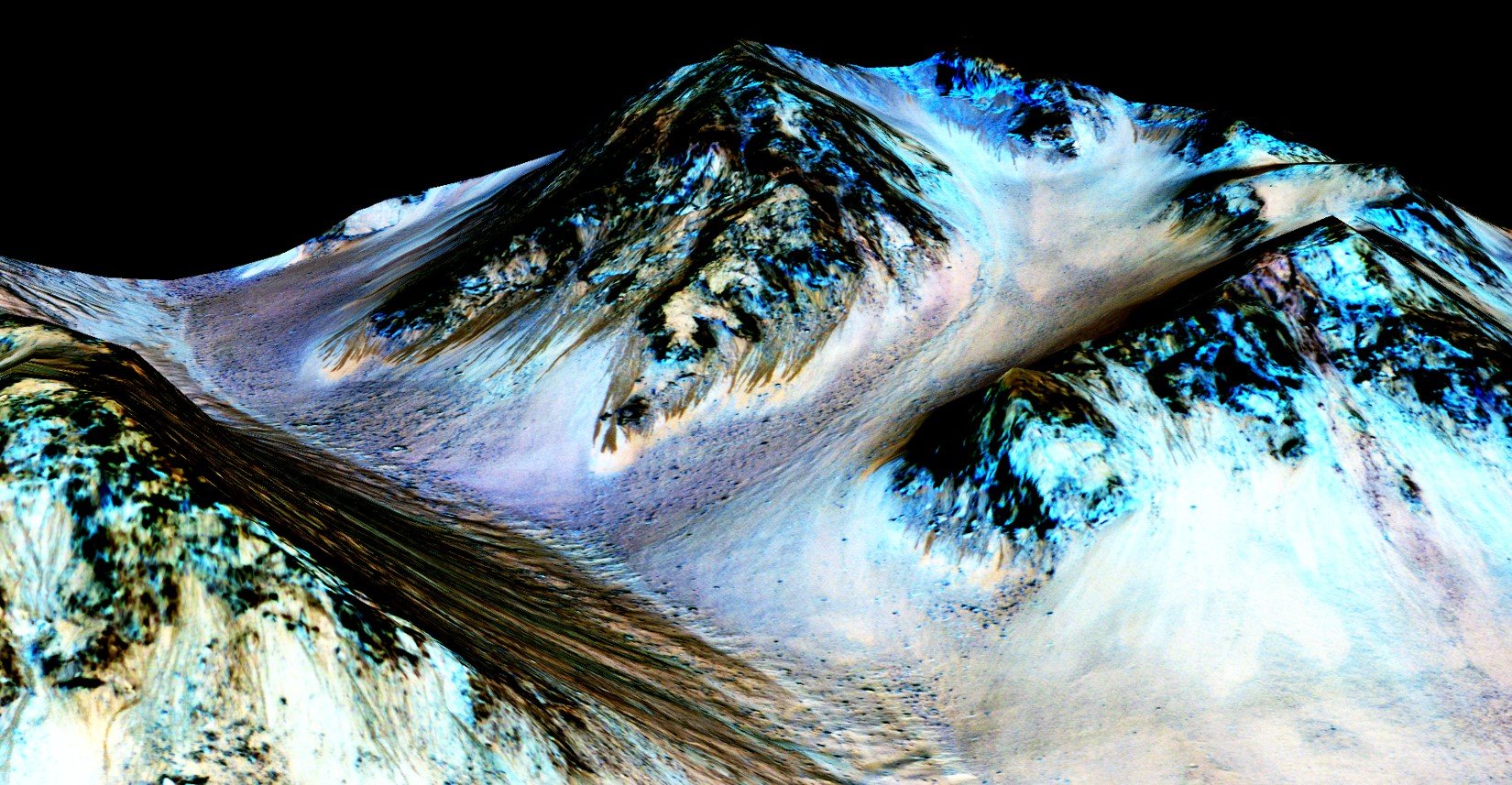
The concept of Recurring Slope Lineae (RSL) has been central to ongoing research. These dark streaks on steep Martian slopes appear seasonally, suggesting the intermittent presence of liquid water. Chevrier’s recent findings indicate that seasonal frosts on Mars may contribute to the formation of brines—saltwater mixtures—by melting and interacting with natural perchlorates found in Martian soil.
Chevrier utilized meteorological data from the Viking 2 mission, which landed in the Utopia Planitia region on September 3, 1976. This area is significant due to its known permafrost and historical connections to a possible ancient ocean. By integrating this data with the Mars Climate Database and advanced computer modeling, Chevrier aimed to assess the conditions necessary for brine formation.
The study reveals a narrow timeframe during which these brines may exist. Specifically, a window lasting approximately one Martian month—equivalent to about two Earth months—occurs between late winter and early spring. During this period, temperatures are optimal for brine formation, with ideal conditions occurring primarily in the late afternoon.
Implications for Life on Mars
While these findings do not offer definitive proof of liquid brines on Mars, they suggest that the planet may support life forms adapted to extreme cold and dryness. The presence of calcium perchlorate, a salt that can lower the freezing point of water, is crucial. This compound solidifies at -75 °C (-103 °F), while average Martian surface temperatures fluctuate from 20 °C (68 °F) during the day to -153 °C (-243 °F) at night.
The research points to the rarity of these brines, as calcium perchlorate constitutes only about 1% of Martian regolith. The thin nature of frost in the Northern Lowlands further complicates the potential for liquid water. Nevertheless, the study opens up exciting possibilities for future Mars missions.
Chevrier’s work was published in Nature Communications Earth and Environment, providing a foundation for further exploration into the presence of liquid water and its implications for extraterrestrial life. As scientists continue to investigate Mars, the findings encourage a reevaluation of the planet’s capacity to support life and suggest that similar processes may occur in other frost-bearing regions across Mars.
These insights not only enhance our understanding of Mars but also shape the goals of upcoming missions, promising to unveil more about our neighboring planet’s potential for hosting life.