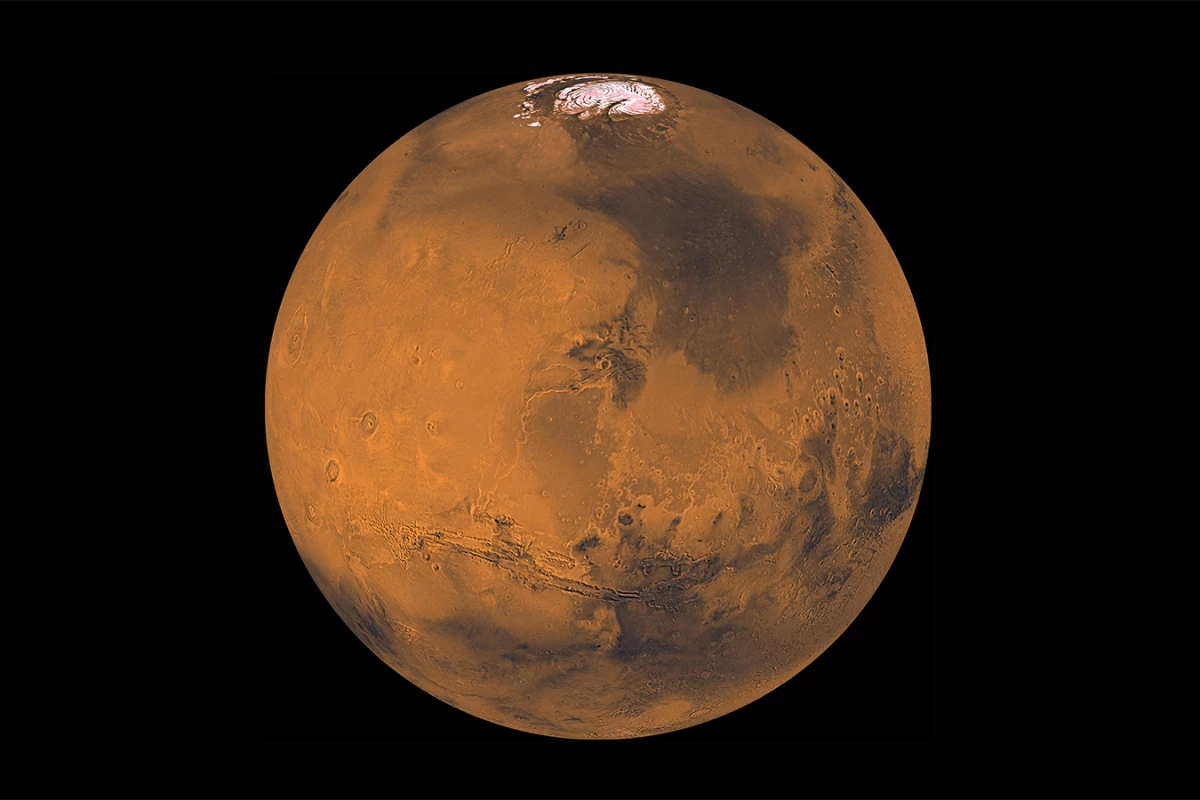
A recent study conducted by researchers from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has revealed that astronauts on Mars would experience time differently than on Earth, effectively “aging” faster due to the effects of time dilation. Specifically, the research suggests that individuals on Mars would age approximately 477 microseconds faster each day compared to their counterparts on Earth.
Understanding Time Dilation and Its Implications
The concept of time dilation stems from Albert Einstein’s Theory of Relativity, which illustrates that time is not a constant. Rather, it is influenced by speed and gravity. For instance, when the first GPS satellites were launched, scientists underestimated how these factors would impact their operational accuracy. As they orbit Earth at 17,500 miles per hour (about 28,000 kilometers per hour), time on these satellites runs faster than on the ground.
Neil Ashby, a key figure in GPS technology, highlighted that without accounting for these time differences, GPS calculations could lead to errors of several miles each day. The intricacies of time measurement in space have become increasingly relevant as humanity plans missions beyond Earth.
Challenges of Calculating Time on Mars
For Mars, the situation becomes more complex. Unlike the Moon, which primarily requires calculations involving the Earth, Moon, and Sun, Mars introduces additional variables. The calculations for time on Mars must consider its own gravitational influence and the elliptical nature of its orbit around the Sun. This complexity adds significant challenges to determining accurate time measurements.
The NIST team, consisting of Ashby and Bijunath Patla, found that Mars’ variable orbital speed causes time to fluctuate by up to 266 microseconds during its year. As a result, the average time on Mars runs 477 microseconds faster than on Earth, necessitating precise adjustments for any future missions or human colonies on the Red Planet.
Addressing these discrepancies is crucial, as astronauts would face a communication challenge akin to an “internet of the Solar System.” Unlike GPS satellites, which can adjust their onboard clocks, correcting time on Mars will involve a more intricate, dynamic system to ensure accurate data transmission and reception.
“It’s good to know for the first time what is happening on Mars timewise,” Ashby commented. He emphasized that this research enhances our understanding of relativity and the fundamental nature of time itself.
The study, published in The Astronomical Journal, marks a significant step forward in our understanding of time as humanity prepares for more ambitious explorations of Mars and beyond. As missions to the Red Planet become more frequent, accounting for these time differences will be vital, not just for scientific accuracy, but also for the well-being of astronauts living and working there.