Research into Mars’ surface composition has revealed the presence of a unique mineral, ferric hydroxysulfate (Fe 3 +SO 4 OH). This discovery offers insight into the planet’s geochemical environment and its historical processes. Scientists have identified this mineral at two significant locations: Aram Chaos and the plateau above Juventae Chasma. Its distinct spectral features, not matching any known terrestrial minerals, have intrigued researchers for over a decade.
Ferric hydroxysulfate forms through the heating of hydrous ferrous sulfates at temperatures exceeding 100 °C. This process results in a strong spectral band at 2.236 μm, which aligns with observations made by the Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars (CRISM) on the Martian surface. The findings suggest that hydrated sulfates at these sites likely originated from evaporative processes or low-temperature alterations, contrasting with the formation of ferric hydroxysulfate, which may indicate heating and oxidation processes.
Geochemical Implications of the Discovery
The implications of detecting ferric hydroxysulfate extend beyond mere mineral identification. This mineral’s existence suggests a complex geochemical history for Mars, characterized by volcanic activity, ash deposition, or hydrothermal processes. Scientists believe these processes could have contributed to the mineral’s formation, indicating that Mars may have experienced dynamic environmental changes over time.
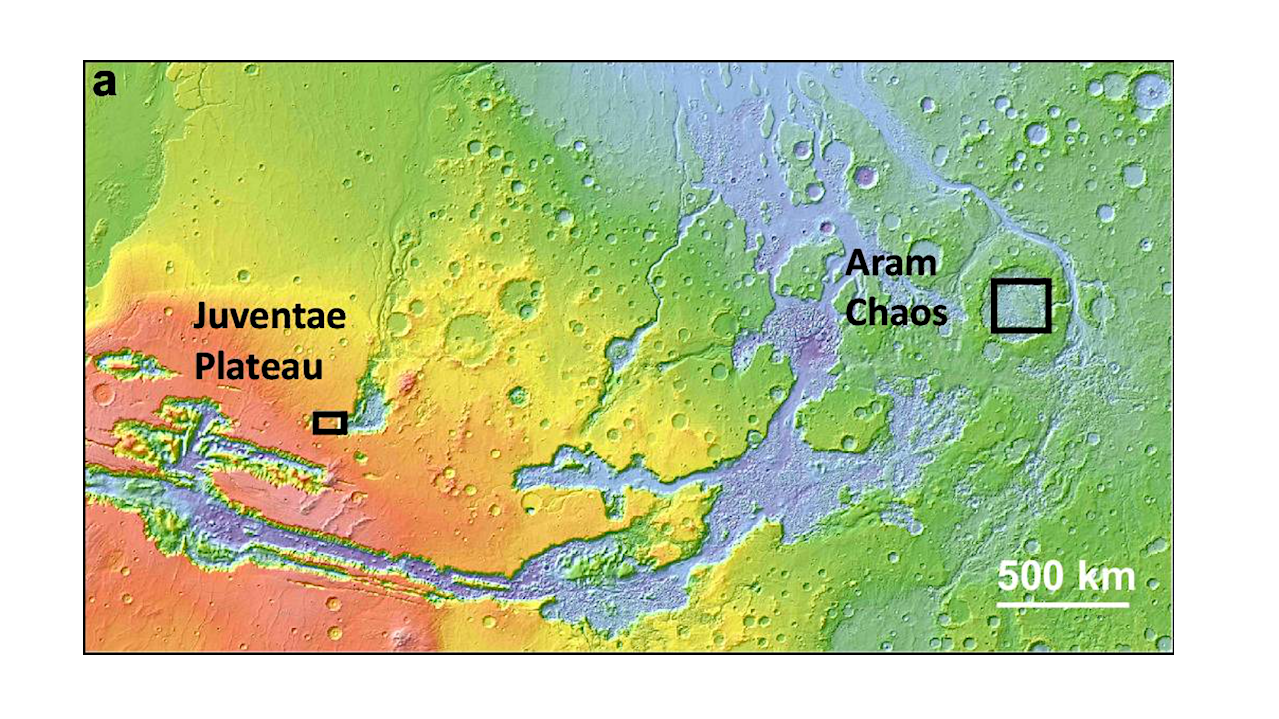
The analysis utilizes data from the Mars Orbital LASER Altimeter (MOLA), which offers a topographic map of the Martian equator, highlighting areas of interest. The Juventae Plateau and Aram Chaos, marked in the MOLA map, show notable elevation differences that may correlate with the geological activity responsible for the mineral’s presence.
Methodology and Findings
The research detailed in the article published by Nature utilizes high-resolution imaging and spectral analysis to characterize the mineral. Using CRISM data, scientists identified the mineral’s spectral signature and compared it to lab spectra of known minerals. Despite extensive comparisons, none of the known minerals provided a good spectral match for the ferric hydroxysulfate-bearing outcrop, underscoring its uniqueness.
The findings contribute to our understanding of Martian geology and provide a foundation for future exploration. As scientists continue to study the composition of Mars, the presence of ferric hydroxysulfate may inform theories about the planet’s habitability and the processes that shaped its surface.
The research not only advances the field of planetary science but also enhances our broader understanding of how planetary environments evolve. Understanding the conditions that led to the formation of minerals such as ferric hydroxysulfate will be crucial in future explorations and potential missions to Mars.