Researchers at the State University of Campinas in Brazil have developed a groundbreaking technique that uses artificial intelligence (AI) to analyze the forces acting on individual grains of sand. This method promises to enhance our understanding of how wind shapes the surface of Mars and other celestial bodies. The findings, published on August 1, 2023, in the journal Geophysical Research Letters, could revolutionize planetary science and engineering applications on Earth.
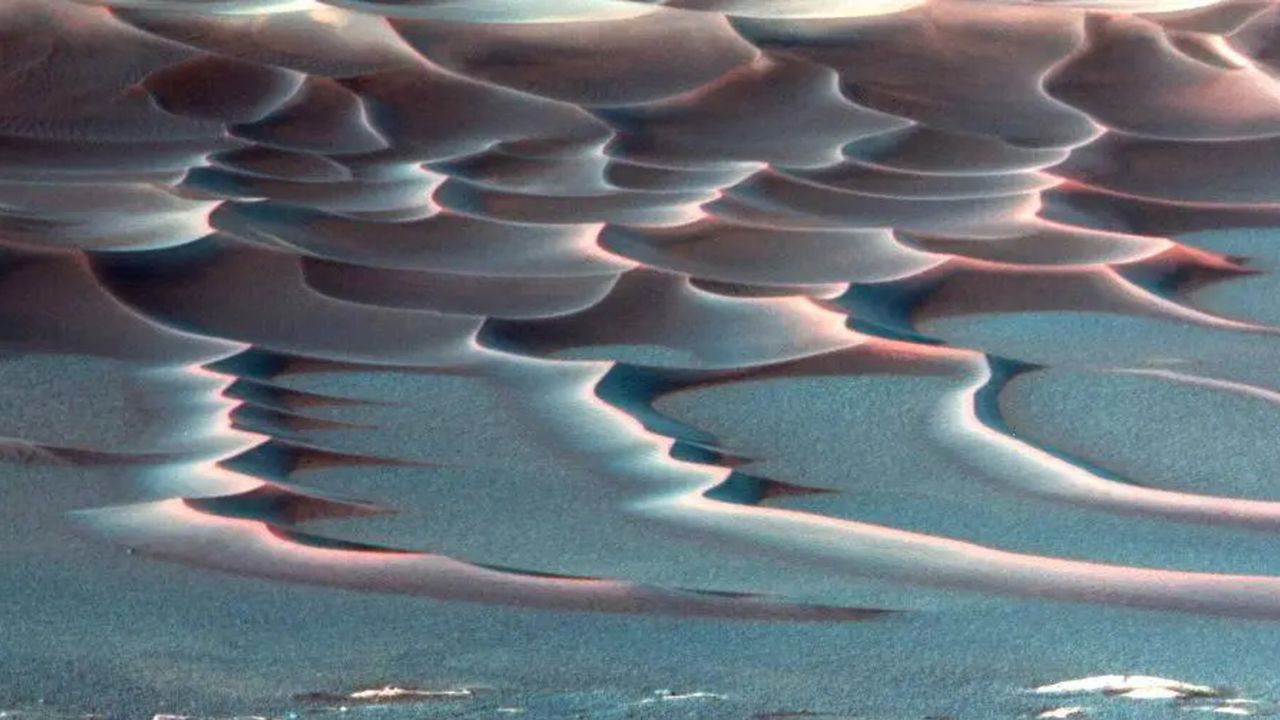
The innovative approach combines laboratory experiments, computer simulations, and AI to create detailed force maps of sand dunes, particularly focusing on the crescent-shaped “barchan” dunes. These formations occur wherever wind or water interacts with loose sand, making them prevalent in both terrestrial deserts and on Martian plains. Until now, measuring the forces driving the movement of each grain of sand had proved to be a significant challenge.
According to the researchers, measuring these forces typically requires placing tiny accelerometers on each grain, a technology that does not currently exist. To address this limitation, the team constructed miniature underwater dunes in a controlled laboratory environment, allowing them to conduct intricate 3D simulations. These simulations calculated the specific forces acting on each grain of sand, creating a comprehensive dataset.
The team then trained a convolutional neural network, a form of AI well-suited for image recognition tasks, to associate the dune images with the corresponding “force maps” generated from their simulations. Once trained, the AI demonstrated the ability to predict force distributions from new images with remarkable accuracy, even for dune shapes it had not encountered in training. “Any granular system that can be seen in an image—whether ice, salt, or synthetic particles—can be analyzed as long as there’s a simulation capable of accurately reproducing the behavior of the material,” explained Renato Miotto, a postdoctoral researcher and lead author of the study.
This technique has significant implications. On Earth, it could assist engineers in predicting coastal erosion, river sediment transport, and the behavior of granular materials used in various industrial applications. Its potential extends to other planets as well, particularly those imaged from orbit, like Mars. The ability to infer past wind intensity and predict future dune evolution based on commonly available images presents a new avenue for understanding the Red Planet’s atmospheric history.
In the words of Erick Franklin, professor and co-author of the study, “It’s possible to infer, from widely available images, the intensity of winds in the past and the evolution of dunes in the future.” This method not only enriches our comprehension of Mars’ surface evolution but also opens new doors for studying planetary atmospheres across the solar system.
As scientists continue to grapple with the complexities of planetary environments, this innovative technique stands to contribute valuable insights into both our own planet and those beyond. The combination of AI and traditional scientific methods exemplifies how interdisciplinary approaches can deepen our understanding of the natural world.