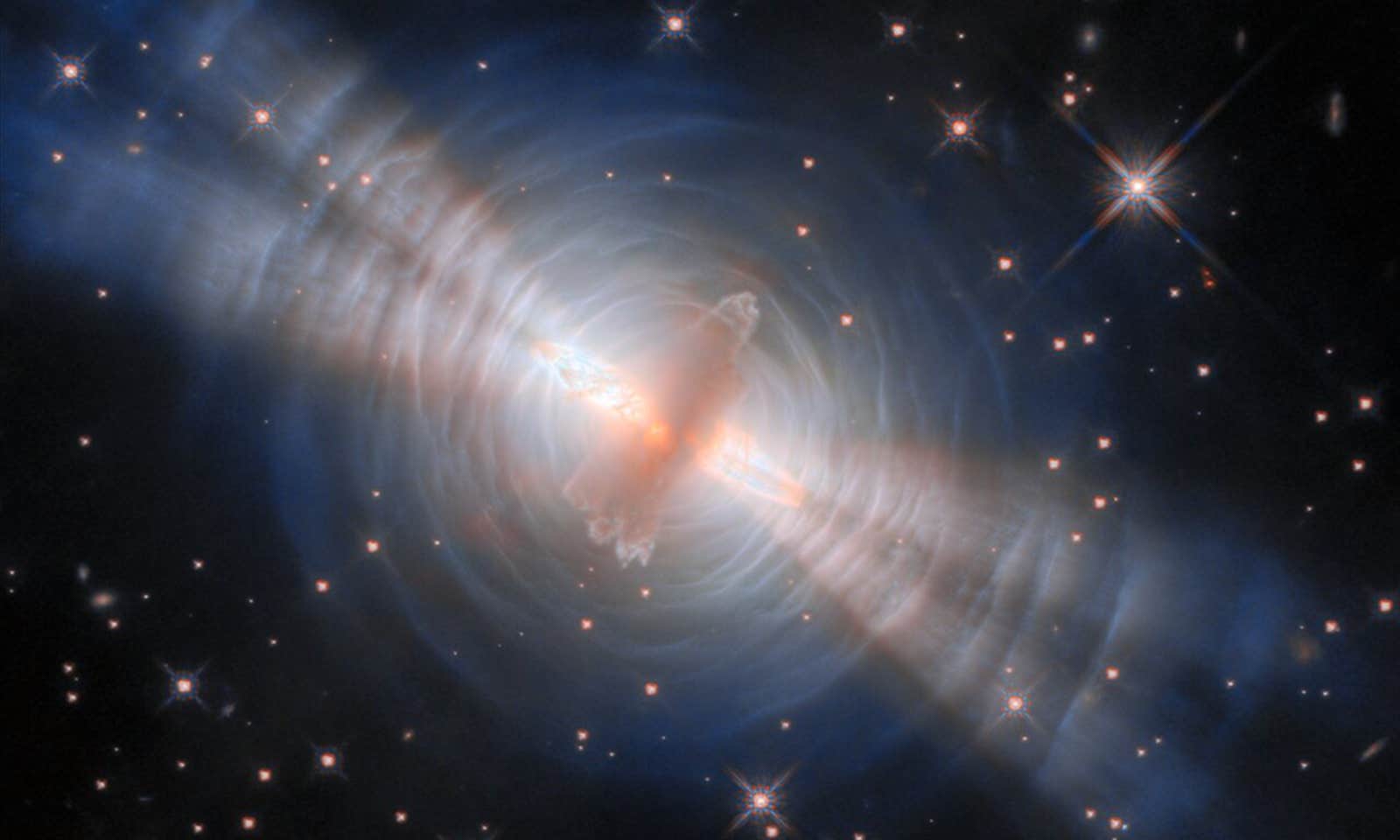
The Hubble Space Telescope has captured breathtaking images of the Egg Nebula, a young nebula enveloping a dying star located in the constellation Cygnus, approximately 1,000 light-years from Earth. This latest observation highlights the nebula’s intricate structure and vibrant colors, offering astronomers a unique perspective on a fleeting astronomical phenomenon.
The Egg Nebula, classified as a pre-planetary nebula, represents a critical transition stage in stellar evolution that lasts only a few thousand years. During this brief cosmic moment, dying stars expel their outer layers, forming luminous clouds of gas that are vital for understanding the lifecycle of stars. The recent images depict twin beams of light emanating from the central star, obscured by a dense disc of stardust. These beams illuminate the surrounding gases, creating a striking visual effect akin to spotlights piercing through fog.
Significance of the Observation
Astronomers are particularly interested in the Egg Nebula due to its rarity and the insights it provides into stellar processes. The nebula’s brief existence offers a valuable opportunity to study the mechanisms at play as stars exhaust their nuclear fuel. The light from the central star reflects off the gaseous surroundings, radiating outward in concentric circles, creating a mesmerizing display that extends approximately one-tenth of a light-year.
Hubble’s capabilities have allowed it to observe the Egg Nebula multiple times, with the first images captured in 1997. Researchers plan to compare these recent photographs with earlier data to analyze the evolution of the star and its surrounding nebula over the decades. This longitudinal study can yield important findings about how such nebulae evolve and the role they play in the formation of new stars and planetary systems.
Aging but Still Effective
At 35 years old, Hubble is now three decades older than its successor, the James Webb Space Telescope. While it may be considered “aging,” Hubble continues to provide invaluable data and stunning imagery, demonstrating that experience can be a significant asset in scientific research. Its longevity and reliability have made it a cornerstone of modern astronomy, offering insights that continue to shape our understanding of the universe.
As the scientific community continues to analyze the Egg Nebula’s latest images, the findings promise to deepen our knowledge of stellar life cycles and the intricate processes that govern the cosmos. The ongoing legacy of the Hubble Space Telescope illustrates how far we have come in our exploration of the universe and the mysteries that remain to be uncovered.