This week has brought significant advancements in our understanding of human evolution, animal behavior, and celestial events. From the discovery of Neanderthals’ early mastery of fire to orca cooperation with dolphins, scientists are uncovering critical insights into both our past and the universe.
Neanderthals and the Control of Fire
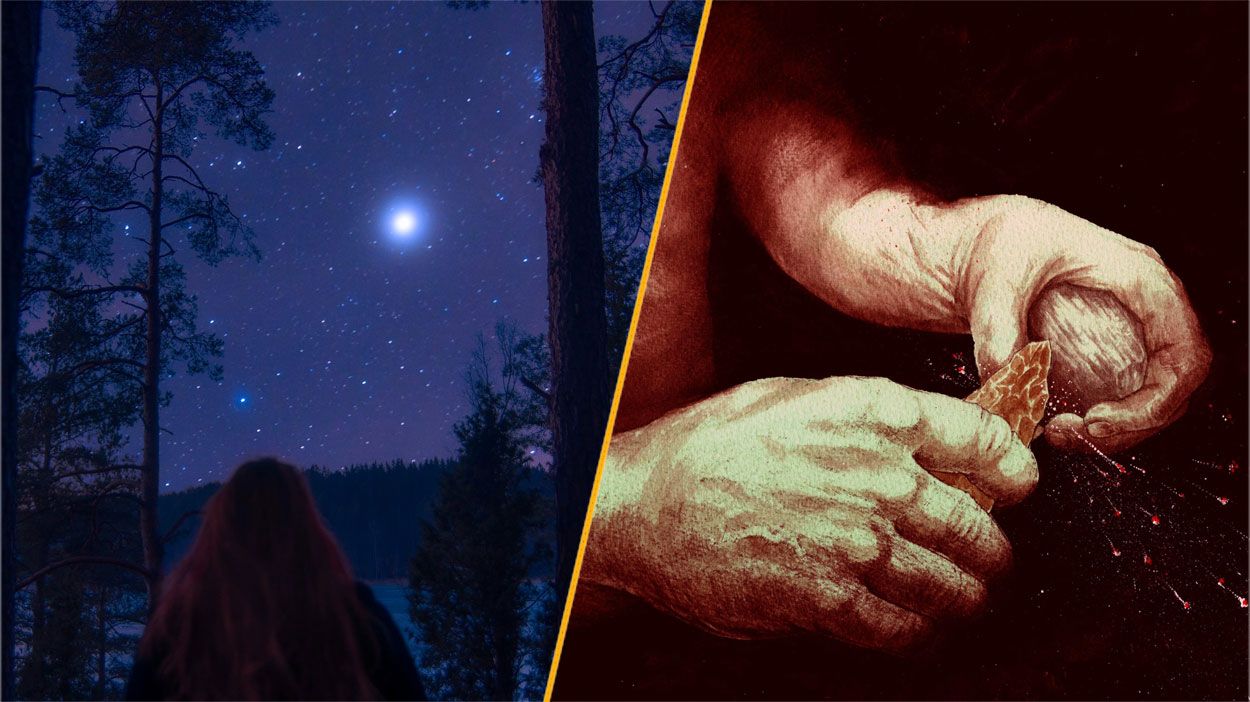
Archaeological research indicates that Neanderthals were capable of making fire as early as 400,000 years ago, significantly earlier than previously believed. A study conducted at a site in Suffolk, England, revealed the presence of pyrite, a mineral that can produce sparks when struck against flint. This finding suggests that Neanderthals intentionally transported the rare mineral to the site for the purpose of fire-making.
The implications of this discovery challenge existing timelines regarding the control and social use of fire by Neanderthals. As paleoanthropologists have long debated the significance of fire in human evolution, this new evidence adds depth to the understanding of Neanderthal culture and their capabilities.
Animal Behavior: Orcas and Dolphins Collaborate
In British Columbia, a study has documented an unusual partnership between orcas and Pacific white-sided dolphins during salmon hunts. Observations show that these marine mammals often collaborate, sharing the spoils of their hunts. The research suggests this behavior could represent the first documented case of cooperative hunting and prey-sharing between these two species.
Despite the findings, not all experts agree on the interpretation of this behavior. Some argue that the interaction may instead be a form of kleptoparasitism, where one species steals food from the other rather than a true collaboration. This debate underscores the complexity of animal interactions and the need for further investigation into their social dynamics.
Cosmic Discoveries and Speculations
In astronomical news, a bright binary star system known as V Sagittae is expected to undergo a supernova explosion within the next century, illuminating the night sky with unprecedented brightness. The flares from this system will be visible to the naked eye, providing a unique opportunity for skywatchers.
Additionally, a mysterious X-ray signal detected from deep space may indicate the disintegration of a star being consumed by two black holes. Such phenomena challenge our understanding of cosmic events and open avenues for further research into the behavior of black holes and stellar evolution.
Meanwhile, a connection has been drawn between Jupiter’s appearance in the night sky and the historical Star of Bethlehem, raising intriguing questions about celestial events during significant historical moments. However, experts caution against definitive conclusions regarding the identity of the Star of Bethlehem.
In a more terrestrial context, a particle detector operated in South Dakota has found no evidence of dark matter, which scientists have been seeking for years. This latest experiment ruled out previous anomalies thought to indicate the presence of dark matter particles.
Insights into the Roman Empire
Recent discoveries at Vindolanda, a historic fort on the northern frontier of the Roman Empire, have reshaped our understanding of life at the edge of Roman Britain. The site, which served as a military outpost for nearly three centuries, has revealed evidence of a vibrant community that reflects the diverse demographics of the empire.
These findings suggest that the Roman frontier was more than just a militarized zone; it was a complex society with interactions among various groups. As archaeologists continue to excavate the site, they are uncovering details that shed light on previously overlooked aspects of Roman history and its societal structures.
This week’s developments in both scientific research and historical archaeology highlight the ongoing quest for knowledge about our world and beyond. From Neanderthals to distant stars, each discovery enriches our understanding of the intricate tapestry of life and history.