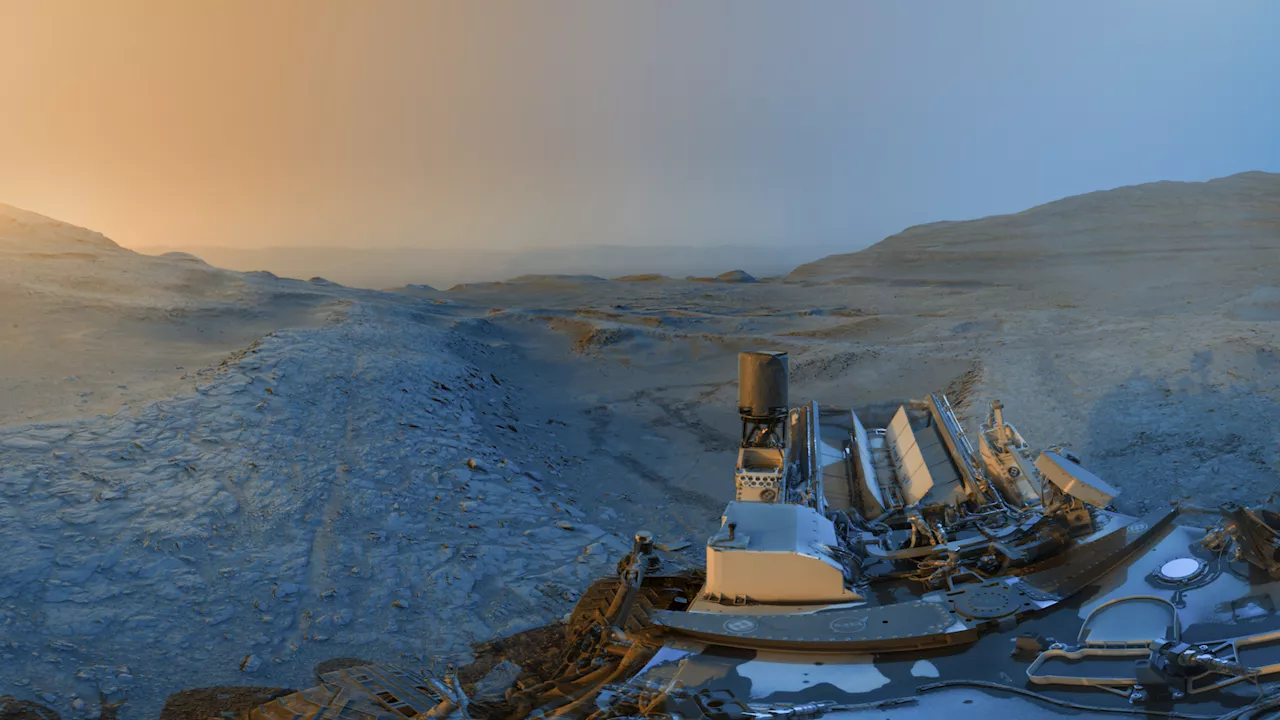
NASA’s Curiosity rover has provided a breathtaking panoramic view of the Martian landscape from the slopes of Mount Sharp, revealing intricate details shaped by ancient water. This latest image, which combines photographs taken over two days in November 2025, showcases the rugged terrain of Gale Crater, illustrating how light changes throughout a Martian day.
The panoramic image, created using data captured on Sol 4,722 and Sol 4,723, features black-and-white photographs taken at different times: one at 16:15 local Mars time and the other at 08:20. By merging these images and applying tinted hues, NASA has enhanced the visibility of various geological features. According to NASA officials, “Adding color to these kinds of merged images helps different details stand out in the landscape.”
Insights from Ancient Water-Shaped Terrain
This area, known for its boxwork formations, provides crucial insights into Mars’ history. The formations consist of mineral-rich ridges that formed when groundwater flowed through cracks in the rock billions of years ago. Over time, wind erosion has exposed these hardened veins, making them a focal point for scientists studying the planet’s environmental evolution. Features like these preserve evidence of ancient water activity, suggesting that Mars was once wetter and potentially habitable.
The Curiosity rover has been diligently exploring these formations and conducting scientific analysis. Recently, it utilized its drill to extract samples from a site named “Nevado Sajama,” located atop a ridge. This panorama captures a view looking north across the boxwork formations and down the slopes of Mount Sharp, with the crater’s rim visible approximately 40 kilometers away. The image also shows wheel tracks from previous drilling activities at a site called “Valle de la Luna.”
Continuing the Mission After More Than a Decade
Curiosity has been on Mars for over 13 years, continuously contributing to our understanding of the planet. The rover’s focus on boxwork terrain and sedimentary layers has been instrumental in piecing together the narrative of Mars’ transformation from a potentially habitable world to the cold, arid landscape observed today.
By analyzing the chemistry and textures of the rocks, scientists are uncovering the history of Mars’ climate changes. Improvements in the rover’s technology allow it to conduct scientific observations while maintaining communication with orbiters overhead, thereby enhancing the efficiency of its operations. These advancements are particularly vital as Curiosity relies on its aging nuclear power source to continue functioning.
As the Curiosity rover continues its exploration, it remains a key asset in the quest to unlock the mysteries of Mars, proving that there are still many stories left to tell about the Red Planet.