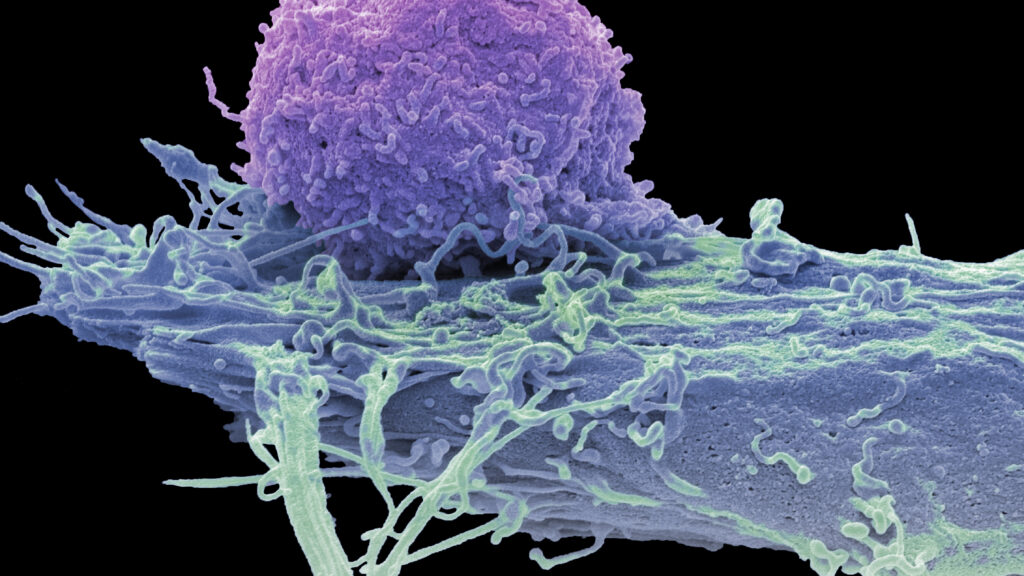
Experimental CAR-T therapies developed by Cabaletta Bio and Bristol Myers Squibb have demonstrated the ability to induce complete remissions in patients suffering from severe inflammatory muscle diseases. These findings, presented during recent dual clinical trials, suggest that personalized cell therapies may extend beyond their current applications in treating blood cancers to offer potential cures for serious autoimmune disorders.
The data, although preliminary, builds on a growing body of evidence indicating the efficacy of CAR-T treatments in addressing complex health issues. Steven Nichtberger, CEO of Cabaletta, emphasized the transformative potential of this therapy. “These are patients who take three to five medicines every day, every week, every month, at great cost both healthwise and financially,” he stated. With a one-time CAR-T treatment, he added, “We’re showing we can eliminate all of those drugs, giving them the opportunity to no longer be patients. We are freeing them from their disease.”
The announcement is significant, as it addresses the pressing need for effective treatments in a demographic that often faces a lengthy regimen of medications. The trials involved patients who had not responded to traditional therapies, highlighting the urgent requirement for innovative solutions in autoimmune disease management.
Impact of CAR-T Therapy on Patients
The implications of these findings extend beyond simple remission. Patients enrolled in the trials reported not only a reduction in symptoms but also a marked improvement in their quality of life. The shift from a lifetime of medication to a single, potentially curative therapy represents a significant advancement in medical treatment.
Currently, many patients with autoimmune disorders are burdened by ongoing health issues and the financial strain of their treatment regimens. Clinical trials have revealed that CAR-T therapy could potentially alleviate this burden, offering a new lease on life for those affected.
The therapies utilize genetically modified T-cells tailored to target specific autoimmune conditions, a process that has seen remarkable success in oncology. This adaptability of CAR-T technology may open new avenues for treatment in various medical fields, particularly for chronic conditions that have remained difficult to manage.
The Future of CAR-T Therapy in Autoimmune Disorders
As research progresses, the medical community is cautiously optimistic about the future of CAR-T therapies in treating autoimmune disorders. More extensive studies will be necessary to confirm these initial findings and to understand the long-term effects of such treatments.
The potential for CAR-T therapy to reduce the need for multiple medications not only promises better health outcomes but also a decrease in healthcare costs for patients. The financial benefits could be substantial, especially considering the high costs associated with long-term medication management.
In conclusion, the preliminary results from the trials conducted by Cabaletta Bio and Bristol Myers Squibb mark a pivotal moment in the treatment of autoimmune disorders. As researchers continue to explore the possibilities of CAR-T therapy, there is hope that these innovative approaches will lead to lasting change in patient care and outcomes.