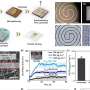
Researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have reported significant advancements in the treatment of relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma through the use of the chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy known as anitocabtagene autoleucel (anito-cel). The latest findings from a Phase II clinical trial demonstrate strong efficacy, suggesting a potential new standard for patients battling this challenging form of cancer.
The Phase II trial results revealed that a substantial proportion of participants experienced a positive response to the therapy. Specifically, data indicates a remarkable overall response rate of approximately 72%, with many patients achieving complete remission. The findings underscore the potential of CAR T cell therapy to transform treatment protocols for multiple myeloma, a disease that has historically posed significant treatment challenges.
Significant Findings and Future Implications
The trial involved patients who had either relapsed after or were refractory to at least three prior lines of therapy. The promising results indicate that anito-cel may be capable of effectively targeting and eliminating malignant cells. These outcomes are particularly noteworthy given the aggressive nature of multiple myeloma and the limited options available for patients who do not respond to conventional treatments.
Dr. Maria V. B. DeAngelo, a lead investigator of the study, emphasized the importance of these findings. “The data from the Phase II trial strongly supports the use of CAR T cell therapy as a viable treatment option for patients with multiple myeloma who have exhausted other therapies,” she stated. Dr. DeAngelo highlighted that the therapy not only offers hope for improved survival rates but also enhances the quality of life for patients facing this illness.
The safety profile of anito-cel also demonstrated a manageable side effect profile, with most adverse events being consistent with those seen in other CAR T therapies. These findings are crucial as they pave the way for further research and potential regulatory approval.
Next Steps in Research and Development
Following these encouraging results, researchers plan to conduct additional studies to further explore the long-term effectiveness and safety of anito-cel. Future trials will also focus on optimizing treatment protocols to maximize patient benefit while minimizing risks associated with therapy.
Given the urgency of improving treatment outcomes for multiple myeloma patients, the research team is hopeful that the findings will lead to broader acceptance and implementation of CAR T cell therapies in clinical practice. The potential for anito-cel to become a critical component of multiple myeloma treatment regimens is a significant step forward in oncology.
As the medical community awaits further developments, the results from this Phase II trial represent a beacon of hope for many patients and their families, illustrating the ongoing commitment to innovation in cancer treatment.