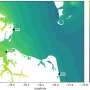
Astronomers have identified signs of an infant planet forming within a cosmic “planet-making factory” located approximately 400 light-years from Earth. This discovery sheds light on the processes involved in planetary formation and offers new insights into the evolution of our galaxy.
The findings come from a study published in IOPScience, where researchers utilized advanced observational techniques to analyze the conditions in a specific region of space. The cosmic factory, rich in gas and dust, provides a fertile environment for the birth of new planets.
Understanding Planetary Formation
The formation of planets is a complex process that involves the accumulation of dust and gas in protoplanetary disks surrounding young stars. In this case, astronomers focused on a particular area where they detected a significant amount of material coalescing into a new planetary body.
According to the research team, the infant planet appears to be in its early stages of development, indicating that the region is highly active with ongoing formation processes. This discovery not only enhances our understanding of how planets like Earth might form but also emphasizes the dynamic nature of our universe.
The characteristics of the forming planet suggest it could be a gas giant similar to Jupiter. Further study will be necessary to determine its exact composition and the implications for understanding the diversity of planetary systems.
Future Implications
This finding could have far-reaching implications for astrophysics and our understanding of the universe. The discovery of new planets contributes to the broader search for potentially habitable worlds beyond our solar system.
Additionally, the research highlights the importance of continuous observation and study of cosmic phenomena. As technology advances, astronomers will be able to gather more data, refining our understanding of planetary formation and the conditions that allow new worlds to emerge.
This discovery underscores the ongoing exploration of space and the quest to answer fundamental questions about the origins of planets and, ultimately, life itself.