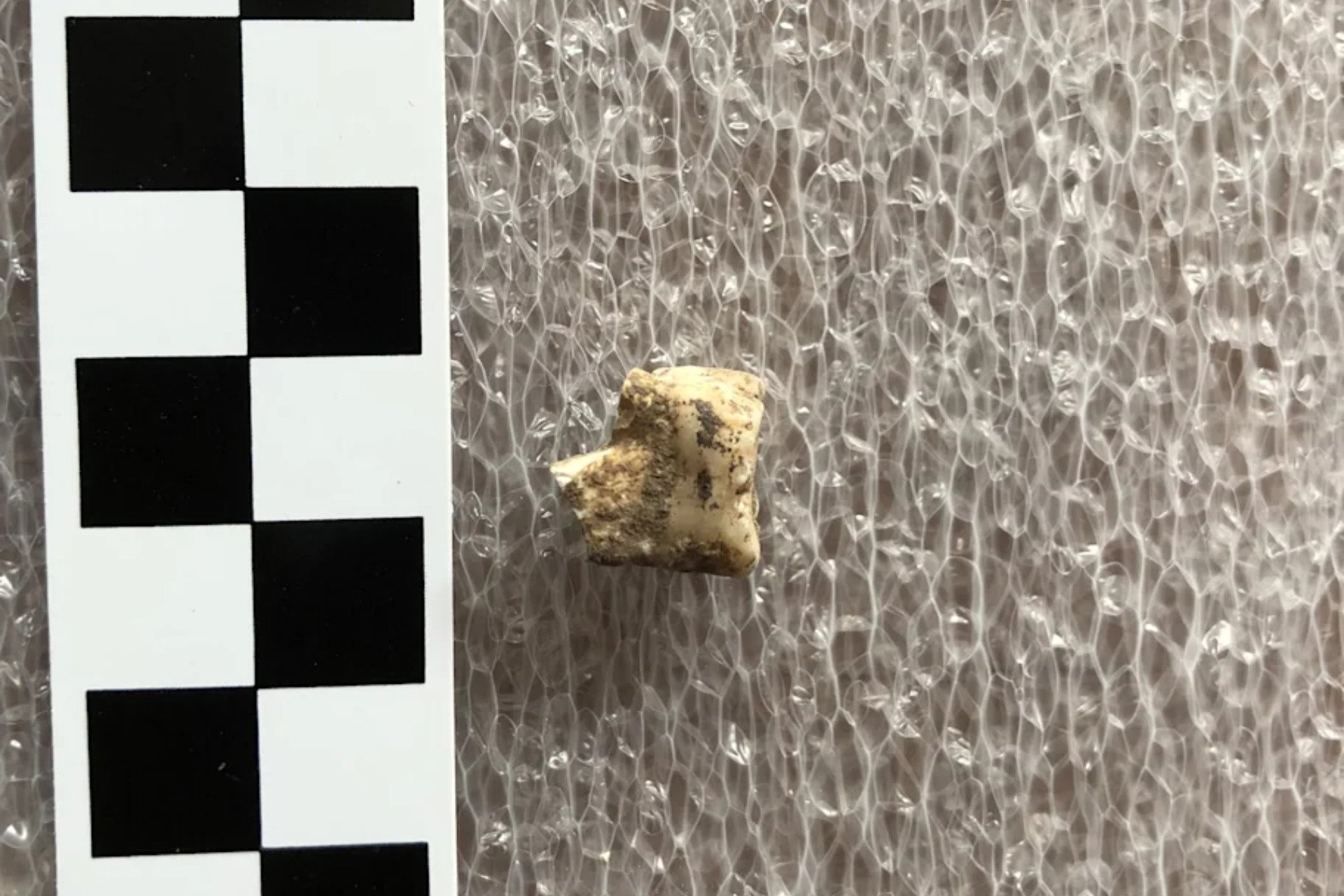
Recent research has uncovered significant evidence indicating that humans were consuming betel nuts as far back as 4,000 years ago. An international team of researchers, led by Piyawit Moonkham from Chiang Mai University, analyzed ancient dental plaque from individuals buried at the archaeological site of Nong Ratchawat in central Thailand. Their findings, published in the journal Frontiers in Environmental Archaeology, shed new light on the long history of this psychoactive substance.
The study focused on dental calculus, a hardened form of dental plaque, from six individuals. By examining 36 samples, the researchers identified organic compounds, specifically arecoline and arecaidine, which are associated with betel nuts. These compounds are also found in other stimulants such as coffee, tea, and tobacco. Moonkham stated, “This is the earliest direct biomolecular evidence of betel nut use in Southeast Asia.”
Innovative Research Techniques Reveal Ancient Practices
To ensure accurate results, the research team created their own betel quid samples, a traditional chewing mixture that includes the areca nut and various other ingredients. “We ground the ingredients with human saliva to replicate authentic chewing conditions,” Moonkham explained. This experimental approach allowed the team to analyze how the components interacted and to confirm the presence of psychoactive compounds in ancient samples.
The significance of this discovery lies not only in its historical value but also in its implications for understanding ancient human behaviors. Shannon Tushingham, senior author of the study and associate curator of anthropology at the California Academy of Sciences, remarked, “In essence, we’ve developed a way to make the invisible visible—revealing behaviors and practices that have been lost to time for 4,000 years.”
While the researchers found evidence of betel nut consumption, they noted an absence of the typical staining that would usually accompany regular betel juice usage. This could be attributed to varying consumption methods or ancient practices related to oral hygiene.
Cultural Significance and Health Implications
The cultural implications of betel nut use are profound. Historically, psychoactive and medicinal plants like betel nuts have played vital roles in community identity and spiritual practices. Moonkham emphasized, “Psychoactive, medicinal, and ceremonial plants are often dismissed as drugs, but they represent millennia of cultural knowledge.”
Despite its long history as a stimulant, frequent betel nut consumption poses health risks, including oral cancers and heart disease. This duality highlights the importance of understanding traditional practices while considering modern health implications.
The research not only contributes to our knowledge of ancient diets but also opens avenues for future studies of human behavior in the absence of conventional archaeological evidence. By analyzing dental calculus, scientists can gain insights into the daily lives of past civilizations, enriching our understanding of their cultural practices.
As the study reveals, the consumption of betel nuts has been a longstanding tradition in Southeast Asia, providing a fascinating glimpse into the lives of people who inhabited the region thousands of years ago.