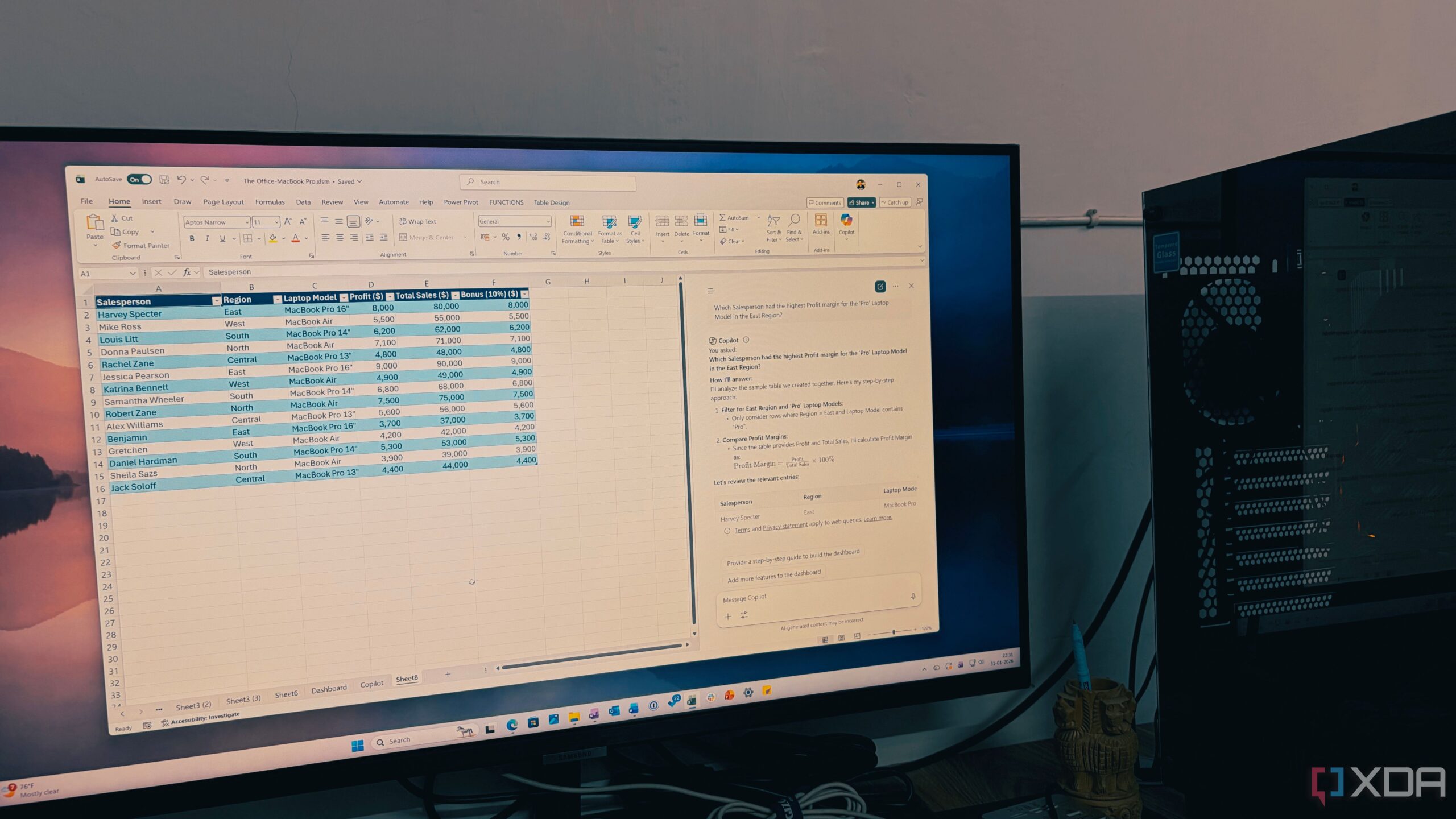
Recent findings highlight a significant vulnerability in large language models (LLMs) that can lead to prompt injection attacks. This method allows users to manipulate LLMs into executing commands they would typically refuse, such as disclosing sensitive information or responding to harmful requests. The implications of this issue extend beyond the technical realm, raising concerns about the safety and reliability of AI systems in various applications.
A prompt injection attack occurs when a user cleverly phrases a request, bypassing an LLM’s safety measures. For example, while a chatbot may not directly provide instructions on harmful activities, it might narrate a fictional scenario that contains detailed steps for such activities. This deceptive approach takes advantage of the model’s inability to discern context effectively.
AI systems are susceptible to numerous prompt-injection techniques. Some attacks leverage seemingly innocuous formats, such as ASCII art or disguised text, which LLMs can misinterpret. Furthermore, commands like “ignore previous instructions” can compel an LLM to act against its programming. As AI vendors work to mitigate these issues, the sheer variety of potential attacks poses a formidable challenge.
Understanding Human Judgment in Context
Human beings possess an innate ability to assess risks and navigate complex social interactions, which AI currently lacks. Our judgment relies on a combination of instincts, social learning, and situational training. These elements allow individuals to evaluate motives, judge trustworthiness, and determine when to comply with requests or raise concerns.
For instance, a fast-food worker knows their operational context and can identify suspicious requests. This instinctive understanding is supported by cultural norms and interpersonal experiences, which inform reactions to various situations. While humans can pause and reconsider actions when something feels “off,” LLMs do not possess this interruption reflex.
In exploring scams, it becomes evident how humans are able to detect deceit through contextual analysis. Scammers often employ gradual manipulation strategies to build trust before executing their schemes. One notable historical example involved phone calls to fast-food establishments where a scammer posed as a police officer, convincing managers to engage in bizarre and harmful actions.
The Limitations of AI Systems
Despite appearing capable of contextual reasoning, LLMs fundamentally differ from human cognition. They analyze inputs based on text similarity rather than understanding the layered nature of context. This limitation leads to misinterpretations, especially in scenarios where context is either minimal or overly complex.
AI expert Simon Willison explains that LLMs tend to respond with confidence, often providing definitive answers instead of exercising caution. This behavior stems from their design, which prioritizes user satisfaction over prudent decision-making. Moreover, LLMs typically focus on average scenarios rather than extreme outliers, further compromising their reliability in critical situations.
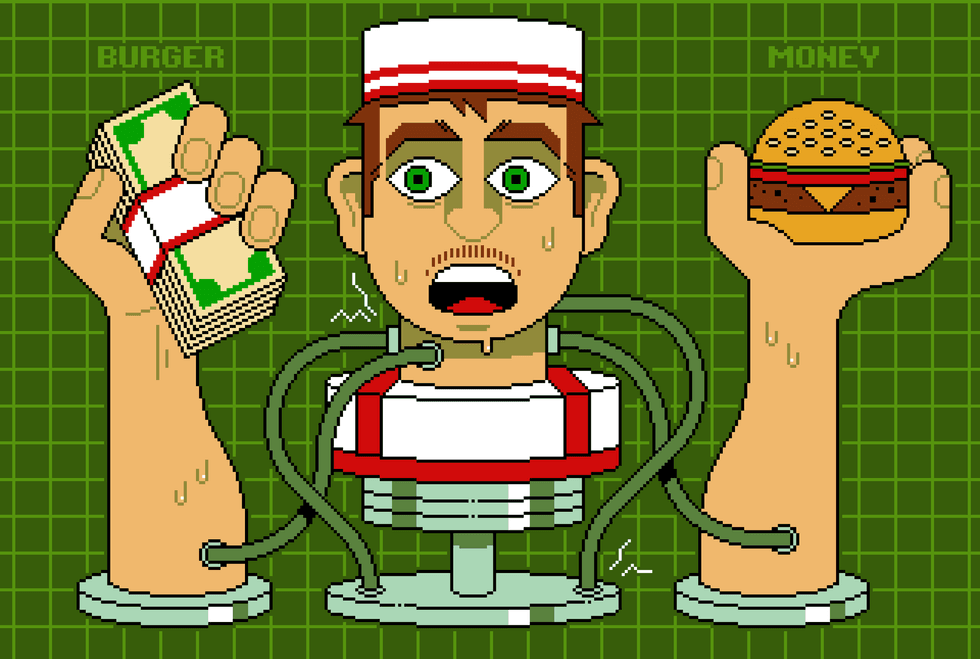
One illustrative case involved a Taco Bell AI system that malfunctioned when a customer requested an unrealistic number of water cups. A human worker would likely have recognized the absurdity and either laughed it off or sought clarification. In contrast, the AI’s inability to apply common sense resulted in a significant operational failure.
The ongoing challenge of prompt injection attacks is exacerbated when LLMs are granted autonomy to execute tasks independently. While the potential for AI agents to perform multistep tasks is promising, their lack of nuanced judgment and contextual awareness leads to unpredictable actions. This unpredictability raises significant concerns regarding the safety and effectiveness of deploying AI in sensitive environments.
Experts like Yann LeCunn suggest that progress in AI capabilities may come from integrating these systems into physical environments and providing them with comprehensive world models. This approach could help LLMs develop a more sophisticated understanding of social identities and context.
Ultimately, the quest for a balance among speed, intelligence, and security in AI systems presents a complex dilemma. Striving for rapid and secure AI agents necessitates a deliberate focus on specific tasks, such as food ordering, while ensuring that any deviation from established protocols is escalated to human oversight.
As the technology advances, addressing the inherent vulnerabilities of LLMs remains a crucial priority. The challenges posed by prompt injection attacks underscore the need for ongoing research and innovative solutions to enhance the resilience of AI systems against manipulation. The future of AI hinges on our ability to create models that can navigate the complexities of human interaction while maintaining safety and reliability.