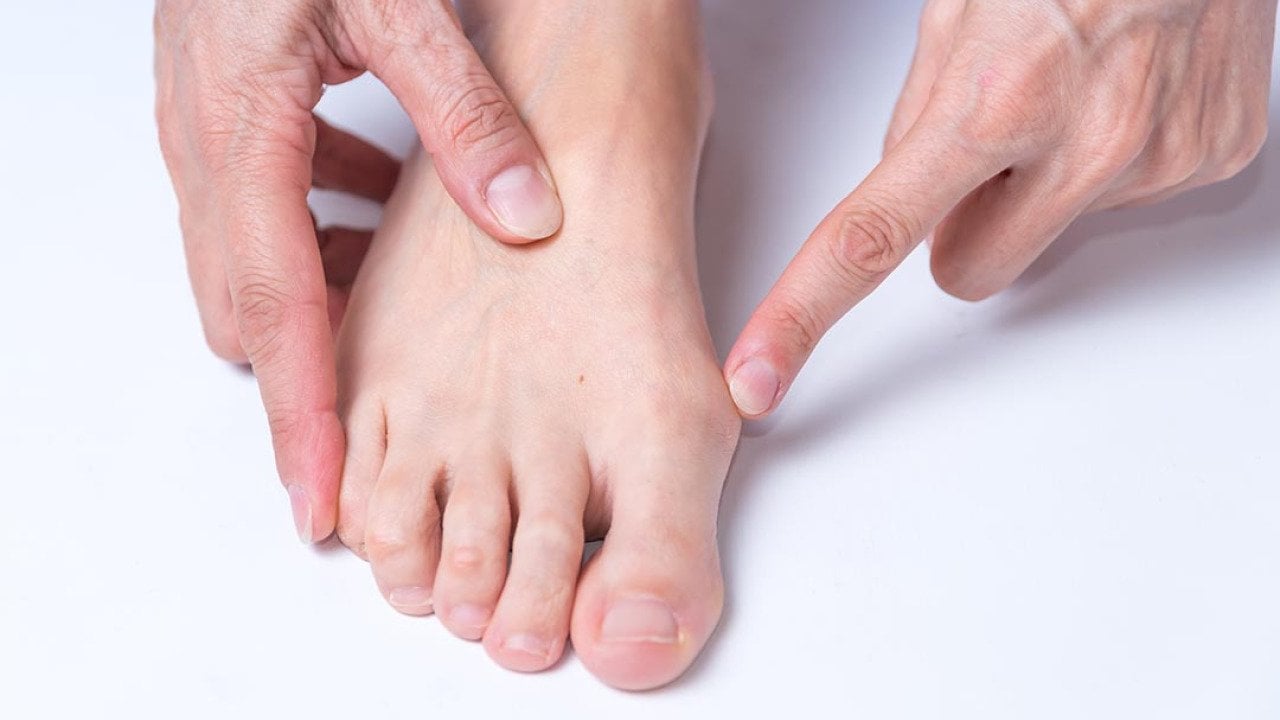
Bunions, characterized by a painful, swollen bump at the base of the big toe, affect many individuals, particularly those over the age of 65. According to Northwell Health, an estimated one in three people in this age group suffers from bunions, which can severely impact mobility and overall quality of life. Understanding this condition is crucial for effective management and treatment.
Understanding the Causes of Bunions
A bunion forms when the bones, tendons, and ligaments in the foot shift out of alignment, often due to prolonged pressure on the metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint. This pressure can cause the big toe to angle toward the other toes, leading to the characteristic bump. Bunions can also develop on the little toe, known as bunionettes or tailor’s bunions.
Genetics plays a significant role in bunion development, with research indicating that approximately 70% of individuals with bunions have a family history of the condition. Additionally, footwear choices can exacerbate the problem. Shoes with narrow toe boxes or high heels can contribute to the inward shift of the toes, particularly in women, who may also experience increased susceptibility due to higher estrogen levels that relax connective tissue.
Recognizing Symptoms and Treatment Options
Bunions can cause significant discomfort, including swelling, pain, and stiffness, making activities like standing or walking painful. Fortunately, not all bunions require surgical intervention. For those with mild symptoms, various nonsurgical treatments can help alleviate discomfort and prevent further progression.
Home treatment options include:
– Wearing shoes with a wide toe box or open toe area.
– Using toe spacers to prevent crowding.
– Applying bunion pads or cushions to reduce pressure.
– Utilizing orthotics, such as arch supports.
– Wearing a bunion splint at night to maintain proper alignment.
Over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications can also provide relief, and in some cases, a doctor may recommend a steroid injection to reduce swelling.
If conservative measures prove ineffective and the pain significantly impacts daily life, surgical options such as a bunionectomy may be necessary. This procedure realigns the toe joint by correcting the underlying bone structure.
The Bunionectomy Procedure: What to Expect
A bunionectomy involves repositioning the bones, ligaments, and tendons surrounding the toe joint. While surgery can improve the appearance of the foot, its primary objective is to relieve pain and restore mobility. Dr. Adam Bitterman, an orthopedic surgeon at Northwell Health, emphasizes that surgery should only be considered when other treatments fail to alleviate pain.
The procedure typically lasts between 30 minutes and 1 hour, with patients often able to return home the same day. Minimally invasive techniques, which use small incisions, can reduce recovery time and pain compared to traditional surgery.
Recovery varies by individual and the specific surgical approach, but many patients can resume partial weight-bearing activities within two weeks and may return to regular shoes in about six weeks. Complete recovery may take up to four to six months, depending on the case.
While bunions can recur if the bones are not correctly realigned or if post-operative instructions are not followed, successful surgery can effectively eliminate the bunion. Consulting a qualified foot specialist is essential for ensuring the most appropriate treatment plan tailored to individual needs.
In summary, bunions are a common foot condition that can significantly affect quality of life. Understanding their causes and treatment options is vital for those affected, allowing them to seek timely and effective care.