Researchers from Osaka Metropolitan University in Japan have revealed that the amyloid-clearing drug lecanemab does not improve the brain’s waste clearance system in the short term. This finding, announced on November 11, 2025, indicates that while lecanemab can reduce amyloid plaques associated with Alzheimer’s disease (AD), it does not restore lost brain function, suggesting a need for a more comprehensive approach to treatment.
The study, led by graduate student Tatsushi Oura and Dr. Hiroyuki Tatekawa, highlights the complexity of Alzheimer’s disease, which affects millions worldwide. The researchers found that even after treatment with lecanemab, patients’ nerve damage persists, and the brain’s natural waste disposal mechanisms remain impaired. These results emphasize that simply targeting amyloid-β (Aβ) may not suffice for effective Alzheimer’s treatment.
Understanding Alzheimer’s and Its Challenges
Alzheimer’s is the most prevalent form of neurodegenerative disorder, characterized by a combination of factors leading to nerve cell damage. One significant contributor is the accumulation of the protein Aβ in the brain. In healthy individuals, a system known as the glymphatic system circulates cerebrospinal fluid, which aids in the removal of metabolic waste, including Aβ. The term “glymphatic” refers to the glial cells that facilitate this essential process.
In individuals with Alzheimer’s, the buildup of Aβ causes arteries to become rigid, impeding the flow of fluids necessary for waste clearance. This disruption hinders the brain’s ability to eliminate toxins, triggering a series of damaging effects that result in cognitive decline.
Findings and Implications of the Research
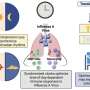
The research team employed a specialized imaging technique known as the DTI-ALPS index to evaluate changes in the glymphatic system before and after lecanemab treatment. Contrary to expectations, no significant improvements were observed in the index three months post-treatment. The conclusion drawn by the researchers indicates that while lecanemab effectively reduces amyloid plaque levels and may slow cognitive decline, it falls short of reversing established neuronal damage and waste clearance issues.
Oura noted, “Even when Aβ is reduced by lecanemab, impairment of the glymphatic system may not recover within the short term.” This suggests that by the time Alzheimer’s symptoms manifest, significant damage may already be done, complicating potential recovery efforts.
The study’s findings call attention to the multifaceted nature of Alzheimer’s, indicating that effective therapies must address multiple biological pathways rather than focusing solely on amyloid clearance.
Moving forward, the researchers aim to explore additional factors, such as age, stage of the disease, and the extent of lesions in white matter. Understanding how these elements interact with the glymphatic system and lecanemab’s effects may lead to enhanced treatment strategies for patients.
The research was published in the Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, contributing to the growing body of evidence regarding the complexities of Alzheimer’s disease and the challenges faced in developing effective treatments.