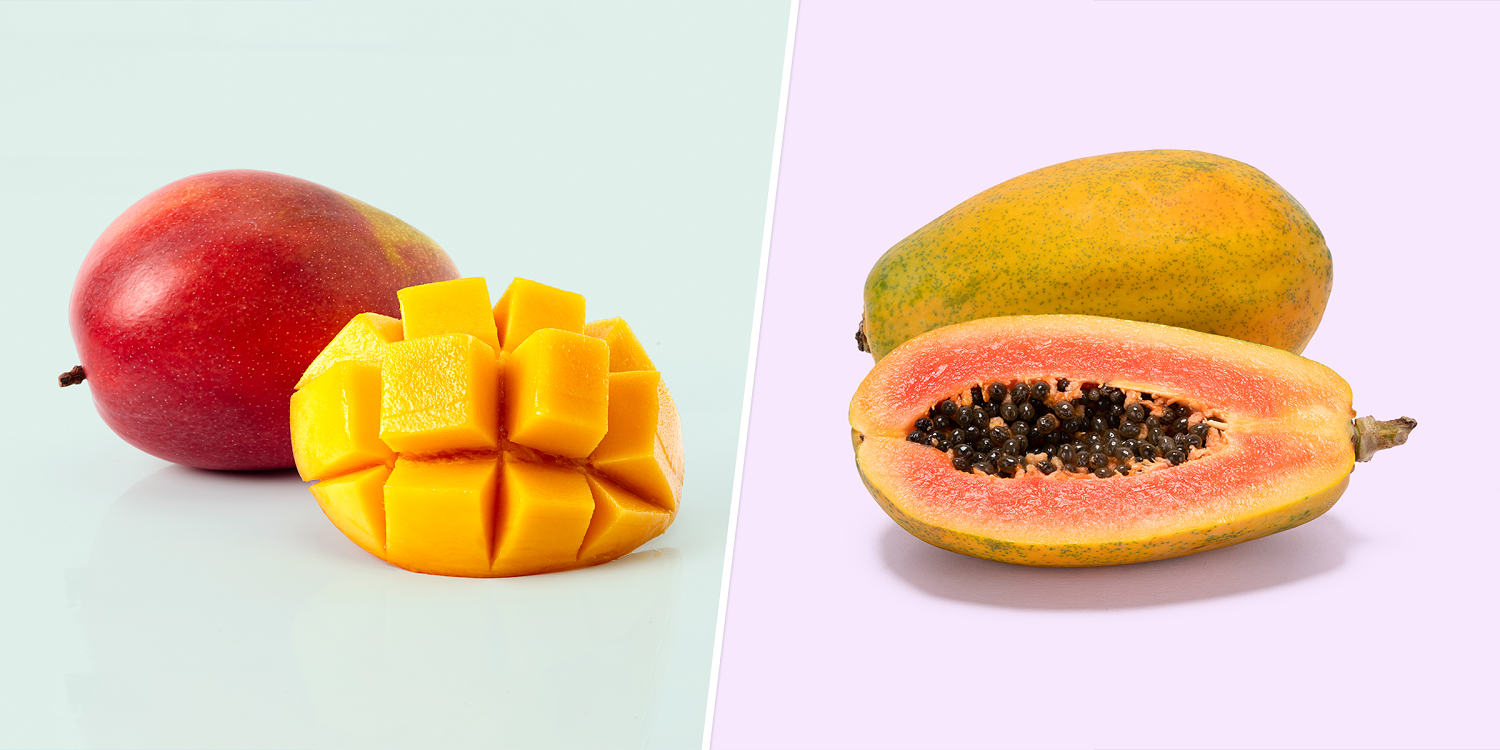
Mango and papaya are two vibrant fruits celebrated for their flavor and nutritional benefits. Both are rich in vitamins and fiber, making them excellent additions to a balanced diet. However, when it comes to specific nutrients, a comparison reveals distinct advantages for each fruit.
Nutrition Breakdown: Mango vs. Papaya
A cup of cut mango contains approximately 99 calories, 1.3 grams of protein, 25 grams of carbohydrates, 2.6 grams of fiber, and 22 grams of sugar. In contrast, a cup of cut papaya has about 62 calories, 0.7 grams of protein, 16 grams of carbohydrates, 2.5 grams of fiber, and 11 grams of sugar. While mango edges out papaya in terms of protein content, neither fruit is a significant source of this nutrient.
Both fruits excel in fiber content, an essential component for digestive health. According to Sarah Rivenburgh, a registered dietitian at OhioHealth, the soluble fiber in mangoes forms a gel in the digestive tract, helping to bind fats and cholesterol, facilitating their removal from the body before absorption. Papaya also offers soluble fiber along with antioxidants and beta-carotene, which the body converts into vitamin A.
Comparative Nutritional Benefits
When analyzing carbohydrate content, mango provides 25 grams per cup, with 22 grams from sugar. In comparison, papaya offers 16 grams of carbohydrates, with 11 grams from sugar. This indicates that papaya is a lower-carb option, which may appeal to those monitoring their sugar intake.
Both fruits are excellent sources of vitamin C, an important antioxidant that supports immune function. A cup of mango delivers 60 milligrams of vitamin C, nearly 70% of the daily recommended value, while papaya surpasses this with 88 milligrams, exceeding 100% of the daily requirement. Both fruits also contribute essential minerals such as magnesium and potassium, with papaya containing double the magnesium of mango.
Mango is particularly high in beta-carotene, providing 1,060 micrograms per cup, compared to papaya’s 397 micrograms. This compound is crucial for maintaining healthy vision and skin. Conversely, papaya contains lycopene, another carotenoid with potential heart health benefits and cancer protection.
Ultimately, the choice between mango and papaya may depend on individual health goals and dietary needs. For those looking to reduce carbohydrate intake, papaya offers a lower-sugar alternative while still providing significant nutrients. However, for those who prefer a fruit without seeds, mango presents a convenient option.
Both mango and papaya can enhance various dishes, from salads to smoothies, contributing not only to flavor but also to overall health. Embracing a variety of fruits, including both mango and papaya, can ensure a well-rounded intake of essential nutrients.
In conclusion, while both fruits are nutritious, understanding their differences can help individuals make informed dietary choices. Whether one chooses the sweetness of mango or the unique flavor of papaya, each fruit offers valuable health benefits that contribute to a balanced diet.