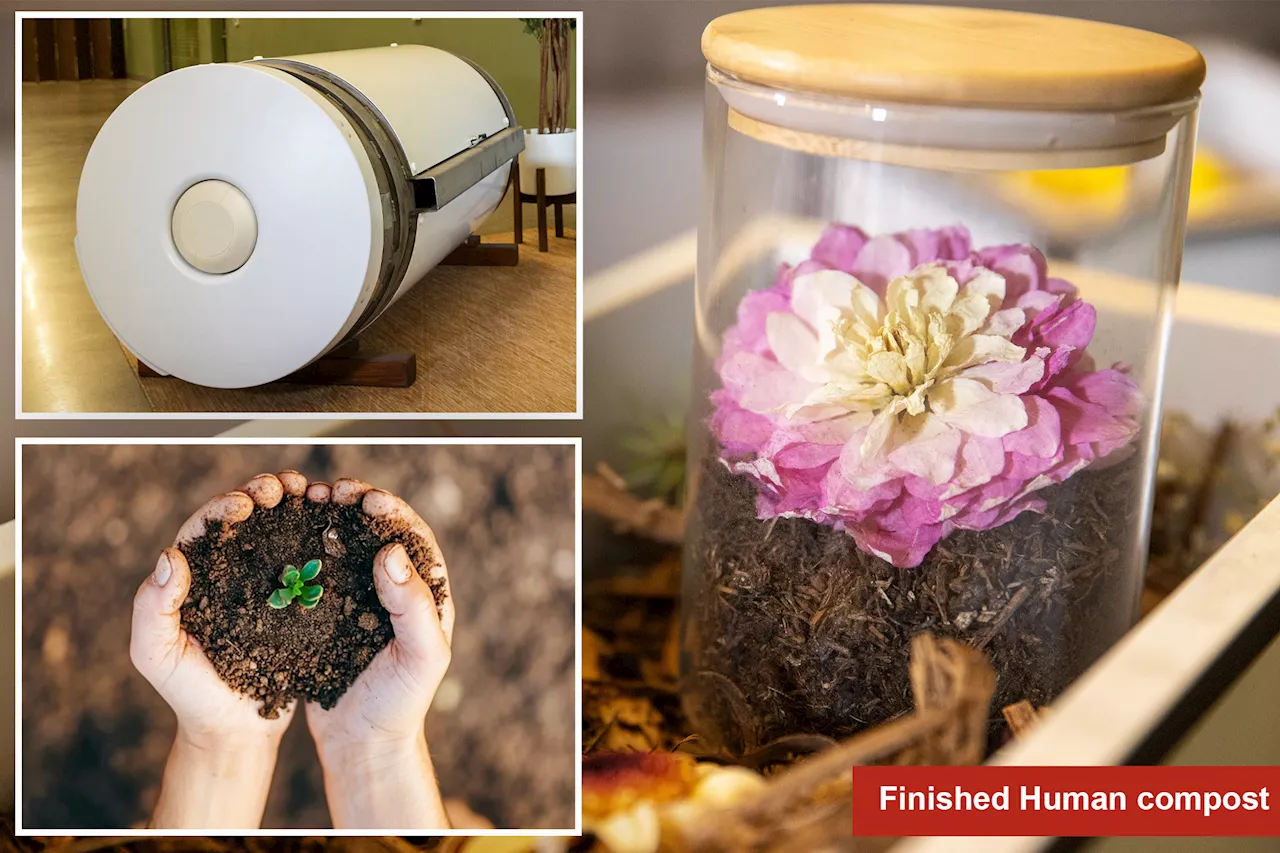
New Jersey has officially legalized human composting, becoming the 14th state in the United States to endorse this environmentally friendly alternative to traditional burial and cremation methods. Governor Phil Murphy signed the law on September 11, 2023, allowing the practice formally known as natural organic reduction, which transforms human remains into nutrient-rich soil.
The legislation aims to provide families with a sustainable option for handling their loved ones’ remains. Natural organic reduction involves placing a body in a specially designed vessel along with organic materials like wood chips and alfalfa. Over a period of several weeks, the body decomposes, resulting in a compost-like substance that can be used to enrich soil. This process not only minimizes the environmental impact associated with conventional burial and cremation but also addresses growing concerns about land use and carbon emissions.
New Jersey’s move aligns with a broader trend across the United States, where more states are exploring innovative options for end-of-life care. As the demand for greener alternatives rises, lawmakers are recognizing the importance of offering choices that reflect changing societal values concerning death and the environment.
Advocates for human composting emphasize its ecological benefits. Unlike traditional burial practices that often involve embalming fluids and non-biodegradable caskets, natural organic reduction provides a way to return nutrients to the earth. This method appeals to environmentally conscious individuals who seek to leave a positive legacy, even after death.
The process has garnered attention in recent years, with states such as Washington, Oregon, and Colorado having previously legalized human composting. The acceptance of this practice highlights a shift in public perception towards more sustainable and holistic approaches to death care.
New Jersey’s decision has been met with support from various advocacy groups and environmental organizations. Many view this legislation as a significant step toward addressing climate change and promoting sustainability. Supporters believe that offering human composting as an option will encourage more people to consider the environmental impact of their choices regarding end-of-life arrangements.
As New Jersey implements this new law, it is expected to establish guidelines and regulations to ensure the process is carried out safely and respectfully. The state will work with industry professionals to create standards that uphold the dignity of the practice while ensuring public health and environmental protection.
With this change, New Jersey not only joins the ranks of states embracing innovative burial alternatives but also positions itself as a leader in promoting sustainable practices. As more individuals and families seek eco-friendly options, the demand for human composting is likely to grow, potentially influencing legislation in other regions.
In summary, the legalization of human composting in New Jersey marks a significant milestone in the evolution of end-of-life care. By adopting this sustainable practice, the state offers a compassionate and environmentally responsible choice for families, highlighting the importance of integrating ecological considerations into all aspects of life, including death.